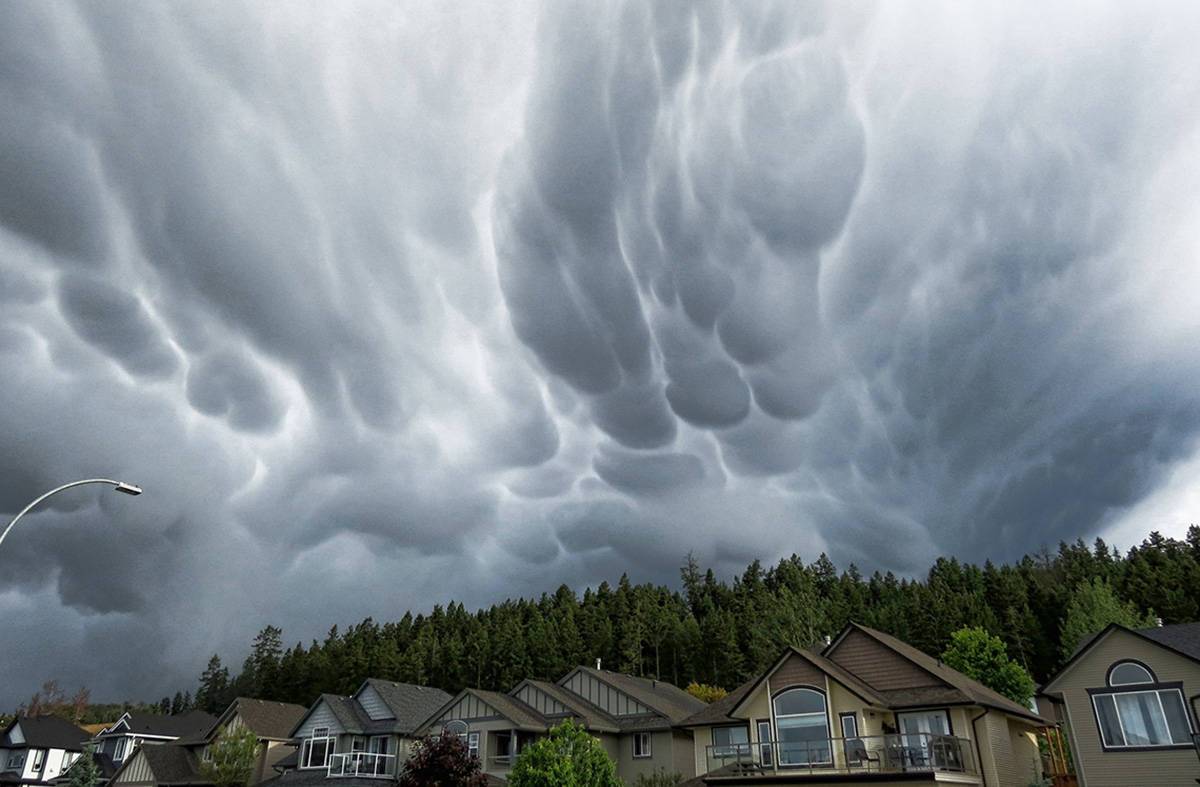
Picture a dark, brooding sky filled with dense clouds. These are cumulonimbus clouds, the towering giants of the atmosphere that bring forth some of nature’s most dramatic displays.
Cumulonimbus clouds are responsible for intense weather events such as heavy precipitation, high winds, and even hail. In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of these storm-producing behemoths.
We’ll explore their formation process under specific tropospheric conditions and how evaporation plays a crucial role in their development. Discover more about the different types of lightning which come from cumulonimbus clouds and how it affects local climate.
Furthermore, we will discuss extreme precipitation events associated with these awe-inspiring cloud formations and how they influence monsoon weather patterns around the globe. Finally, prepare to be captivated by tales of flash floods induced by cumulonimbus activity and discover valuable learning resources to further your knowledge on this intriguing subject.
So buckle up as we embark on an atmospheric adventure through the powerful realm of cumulonimbus clouds!
Formation of Cumulonimbus Clouds: A Journey into the Troposphere
Are you ready for an adventure?
We’re about to dive deep into the world of cumulonimbus clouds and explore their fascinating formation process.
Let’s start with a quick overview:
Tropospheric Conditions for Cumulonimbus Development
The troposphere is where all the action happens. Cumulonimbus clouds develop in this lower part of Earth’s atmosphere, typically beneath 20,000 ft., thanks to certain conditions that make it just right for these towering giants.
Role of Evaporation Processes in Cloud Formation
You might be wondering how these colossal clouds come to life. Evaporation processes are key in forming cumulonimbus clouds, transforming water vapor into droplets or ice crystals. Fascinating stuff.

Influence of Greenhouse Effect on Cumulonimbus Clouds
But wait, there’s more. The greenhouse effect also has its hand in shaping these awe-inspiring cloud structures. Trapping heat within our planet’s atmosphere helps create turbulence and drive weather patterns associated with cumulonimbus clouds.
Now that we’ve covered some basics let me share some interesting facts you may not know:
- Cumulus clouds are often referred to as “fair-weather friends,” while their larger counterparts, cumulonimbus clouds, are known for bringing intense storms and heavy precipitation.
- These cloud formations can reach heights of up to 60,000 ft. or more. That’s higher than Mount Everest.
So there you have it – a whirlwind tour of the formation process behind these magnificent weather-makers. Discover more about cumulonimbus clouds by taking a look at our comprehensive guide. Prepare to be amazed by nature’s incredible power.
Characteristics and Types of Lightning Produced by Cumulonimbus Clouds
Let’s talk about lightning.
Cumulonimbus clouds are known for their lightning-producing abilities, but have you ever wondered how it all works? Allow me to enlighten you.
Intracloud Lightning Explained
The most common type of lightning is intracloud, which occurs within the cloud itself. This fascinating phenomenon happens when a strong precipitation shaft forms below the base of cumulonimbus clouds, transferring negative charge to upper positive regions within storms. Intracloud lightning is responsible for those bright flashes we see during thunderstorms – pretty electrifying stuff.
Impact on Regional Weather Patterns
Wondering how this affects our weather? Intracloud lightning plays a significant role in creating right-moving storm systems that can impact large areas’ weather patterns.
- Rain: These storm systems often bring heavy rainfall, sometimes causing flash floods (more on that later).
- Hail: Hailstones form as ice particles grow larger while being carried upward by powerful updrafts. Ouch.
- Tornadoes: In some cases, these storms may even spawn tornadoes – nature’s most violent windstorms. Hold onto your hats.
To sum it up: The next time you’re watching a thunderstorm, remember that the lightning you see is not only an awe-inspiring spectacle but also plays a crucial role in shaping our weather patterns.
Overdeveloped cumulus congestus clouds can form into cumulonimbus clouds, which are dense storm clouds that produce lightning, heavy precipitation, and wind shear. These clouds form when warm, moist air rises and cools, causing water vapor to condense into ice crystals.
The atmosphere closest to the Earth’s surface is heated by the sun, causing the air to rise and creating a low-pressure zone. The warm air ascends, cooling and causing the vapor to condense into tiny ice crystals that form a cumulus cloud. If the cumulus cloud continues to grow, it can become a cumulonimbus and bring hail.
Cumulonimbus clouds can produce hail, which is formed when water droplets freeze and are carried up and down by strong updrafts. The hailstones grow larger as they are coated with more layers of ice. These clouds can also produce lightning, which is caused by the buildup of electrical charges within the cloud. When the charges become too great, they are discharged as a bolt of lightning.
Cold front squall lines can also produce cumulonimbus clouds, which can cause severe thunderstorms. These storms can produce high winds, heavy rain, and lightning. It’s important to stay indoors during a thunderstorm to avoid being struck by lightning.
Now go out there and impress your friends with your newfound knowledge of cumulonimbus clouds and lightning.
Key Takeaway:
Cumulonimbus clouds are known for producing lightning, specifically intracloud lightning, which occurs within the cloud itself. This type of lightning plays a significant role in creating right-moving storm systems that can impact weather patterns and cause heavy rainfall, hailstorms, and even tornadoes. It’s important to stay indoors during thunderstorms to avoid being struck by lightning.
Extreme Precipitation Events Associated with Cumulus & Cumulonimbus Clouds
Mesoscale Convective Systems (MCS), which are associated with cumulus and cumulonimbus clouds, have the potential to cause extreme precipitation events that can drastically affect Earth’s climate system.
MCS is responsible for extreme precipitation events that can significantly impact Earth’s climate system, including hydrologic cycles, net radiation budgets, latent heat measurements, and global warming trends. To gain a better understanding of MCS and its impacts on Earth’s climate system, please refer to the linked resource.
Effects on Earth’s Climate System
Heavy rainfall from these cloud formations can lead to flooding in affected areas. This not only disrupts the lives of people living there but also affects ecosystems and contributes to soil erosion.
Duration Variations Based on Atmospheric Factors
The average duration of heavy rainfall events is around 20 minutes; however, this may vary depending on atmospheric conditions at play during a particular event. In some instances, the duration of heavy rainfall events may deviate from the expected 20 minutes due to atmospheric conditions.
A Quick Recap:
- Cumulus and cumulonimbus clouds contribute to extreme precipitation events through Mesoscale Convective Systems (MCS).
- MCS have significant impacts on Earth’s climate system, such as hydrologic cycles, net radiation budgets, latent heat measurements, and global warming trends.
- The duration of heavy rainfall varies based on atmospheric factors present during an event.
Now that you’re well-versed in extreme precipitation events let’s move on to how monsoon weather patterns are influenced by developing storms.
Monsoon Weather Patterns Influenced by Developing Storms
To understand the impact of cumulonimbus clouds on monsoon weather patterns, we need to explore the fascinating world of downdrafts and their role in shaping regional climates.
Ready? Let’s go.
Downdraft Roles in Monsoonal Circulation
The key player here is a phenomenon called downdraft, which refers to powerful downward currents of air within developing storms.
In simple terms, these downdrafts push cooler air from higher altitudes down toward the ground, where it spreads out and influences local weather conditions.
This process can significantly affect monsoonal circulation and contribute to extreme rainfall events during the monsoon season.
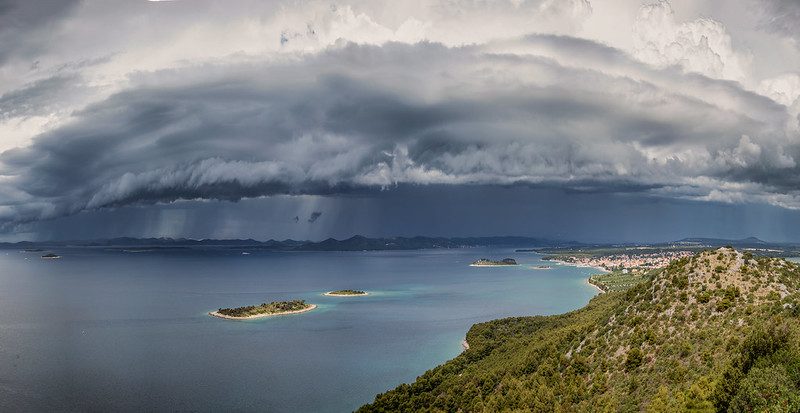

Impacts on Regional Weather Patterns
Let’s now explore the consequences of downdrafts on regional weather patterns during monsoon season.
Cumulonimbus clouds with strong downdrafts can lead to sudden changes in wind direction and intensity – this is known as a gust front.
- Gust fronts often result in heavy rainfall accompanied by thunderstorms or even hailstorms.
- In some cases, they may cause localized flooding due to the rapid accumulation of water.
- All these factors combined make for an unpredictable yet fascinating display of nature’s power during monsoon season.
Gain more insight into the effects of cumulonimbus clouds on weather patterns by visiting the National Weather Service’s informative resource.
Check out this informative resource from the National Weather Service.
Now you’re equipped with knowledge about how developing storms, downdrafts, and cumulonimbus clouds influence monsoon weather patterns.
Stay curious and keep exploring the fascinating world of meteorology.
Flash Floods and Cumulonimbus Clouds: A Stormy Relationship
Imagine this scenario: you’re enjoying a sunny day when suddenly, dark clouds appear on the horizon, bringing with them torrential rain and flash floods. What’s going on?
Scale Comparison to River-Based Flooding
In fact, flash floods caused by cumulonimbus clouds can be just as destructive as those occurring near major rivers or wide flood plains. These floods often occur without warning and develop quickly due to heavy rainfall within a short period of time. The abrupt rush of H2O can result in risky scenarios, for example, road obstructions, landslides, and even fatalities, if people are taken aback by the ascending waters.
In addition to immediate dangers during flooding events, communities may face long-term consequences, including property damage and infrastructure repair costs. To better understand how cumulonimbus clouds contribute to flash flooding risks, check out this informative article from the National Weather Service.
Now that we have a basic understanding of how cumulonimbus clouds can lead to flash floods, let’s look at how you can stay prepared.
Step #1: Stay informed about local weather conditions and pay attention to any flood warnings or watches issued in your area.
Step #2: Create an emergency plan with your family, including evacuation routes and meeting points in case of a sudden flooding event.
Step #3: Keep essential supplies on hand, such as non-perishable food items, bottled water, first aid kits, and important documents stored in waterproof containers.
It’s important to note that cumulonimbus clouds are dense storm clouds that form from overdeveloped cumulus congestus clouds. The Latin term “cumulus” means “heap” or “pile,” and “nimbus” means “rain.”

These clouds are often associated with cold front squall lines and can produce lightning, heavy precipitation, hail, and high winds due to wind shear. They form when water vapor and ice crystals in the atmosphere closest to the Earth’s surface combine to create a towering cloud that can reach heights of up to 10 miles.
While cumulonimbus clouds can be beautiful to look at, they can also be dangerous. By staying informed and prepared, you can help protect yourself and your loved ones from the risks associated with flash floods caused by these powerful clouds.
For additional tips on how to stay safe during a flash flood or other emergency, visit Ready.gov’s detailed guide.
Key Takeaway:
Cumulonimbus clouds can cause flash floods that are just as destructive as those caused by major rivers or floodplains. It is important to stay informed and prepared for these sudden flooding events, including creating an emergency plan with your family and keeping essential supplies on hand. Remember, cumulonimbus clouds may be beautiful, but they can also be dangerous, so it’s better to be safe than sorry.
7 Types Of Clouds Associated With A Cumulonimbus Thunderstorm Cloud
Cumulonimbus clouds are the type of clouds that are associated with thunderstorms and can produce hail, thunder, and lightning. These clouds are dense, towering vertical clouds that form from water vapor condensing in the lower troposphere and build upward, carried by powerful buoyant air currents. Cumulonimbus clouds can form alone, in clusters, or along squall lines.
There are several types of clouds associated with cumulonimbus thunderstorm clouds, including:
- Shelf clouds (arcus cloud feature): These clouds are low, horizontal clouds that form along the leading edge of a thunderstorm.
- Wall clouds (murus cloud feature): These clouds are low, rotating clouds that form beneath the base of a thunderstorm.
- Tail clouds attached to the wall cloud (cauda cloud feature): These clouds are low, horizontal clouds that form behind a wall cloud.
- Beaver tail cloud that acts like a river of moisture feeding into the storm (flumen cloud accessory): These clouds are low, horizontal clouds that form behind a thunderstorm and feed moisture into the storm.
- Anvil cloud (incus cloud feature): These clouds form above the main cumulonimbus cloud, where the cloud hits the top of the troposphere and spreads out across the sky.
- Scud Clouds: Scud clouds are low, ragged, and wind-torn clouds that often form in the wake of a cold front or thunderstorm and are typically associated with precipitation.
- Mammatus Clouds: Mammatus clouds are pouch-like structures that form beneath the base of a cloud, typically a cumulonimbus raincloud, and are composed primarily of ice but can also be a mixture of ice and liquid water or be composed of almost entirely liquid water. They are formed by sinking cool air.
It’s important to note that cumulonimbus clouds can produce severe weather, such as tornadoes, hazardous winds, and large hailstones. If you observe these clouds, it’s best to stay informed on the latest forecasts and weather alerts.

Learning Resources for Cumulonimbus Clouds: Expand Your Knowledge and Become an Expert
If you’re eager to learn more about cumulonimbus clouds or other related topics, there are plenty of resources available online that can help quench your thirst for knowledge.
And guess what? I’ve compiled a list of some fantastic sources just for you:
- Universe Today: A comprehensive website covering various aspects of space and Earth sciences.
- USA Today Weather offers up-to-date news, forecasts, and insights about the atmosphere from a renowned American publication.
- University of Illinois Website: Dive into detailed explanations of cloud formation processes with their Meteorology Guide section.
- Astronomy Cast: Listen to engaging podcasts discussing various topics related to astronomy and Earth science.
By exploring these informative resources, not only will you expand your understanding but also establish yourself as an expert source among friends and family members who share similar interests.
Bonus tip: You can even create content based on what you’ve learned – write blog posts or make videos explaining fascinating facts about cumulonimbus clouds or other meteorological phenomena. This way, others can benefit from your knowledge, and you’ll attract a wider audience.
So go ahead, dive into these resources, and embark on an exciting journey to become a cumulonimbus cloud connoisseur. Happy learning.
FAQs in Relation to Cumulonimbus Clouds
What are 5 facts about cumulonimbus clouds?
- Cumulonimbus clouds are associated with thunderstorms and heavy precipitation.
- They can reach heights of up to 60,000 feet, often extending into the stratosphere.
- These clouds produce various types of lightning, including intracloud and cloud-to-ground strikes.
- Cumulonimbus clouds form due to overdeveloped cumulus congestus clouds and are characterized by their dense, towering appearance.
- Finally, these powerful storm systems can contribute to extreme weather events like flash floods.
What Is The Anvil On A Cumulonimbus Cloud?
An anvil cloud, also known as a cumulonimbus incus, is a type of cloud that forms in the highest levels of thunderstorms or cumulonimbus clouds. It is made of ice particles that have frozen in the upper parts of the cloud. The name “anvil” comes from its similar look to a tool that is used by metal workers.
The cool shape that you see with the flat top is due to rising air in storms. The air expands and spreads out as the air hits the bottom of the stratosphere. The air that rises from the anvil is cooler than the air of the stratosphere. This prevents the air from the anvil from rising beyond the stratosphere.
Anvil clouds can be spotted many miles away and are often seen over 100 miles away.
Sometimes, these thunderstorm tops can be seen over 100 miles away. On some occasions, you may be able to see streaks of snow called “virga,” which falls from the outer part of an anvil.
Anvil clouds are generally found in strong thunderstorms and are characterized by their icy, anvil-shaped top.
They exist through the entire height of the troposphere and are the only cloud type that can produce hail, thunder, and lightning.

Why are cumulonimbus clouds important?
Cumulonimbus clouds play a crucial role in Earth’s climate system by redistributing heat and moisture through convection processes. They also influence regional weather patterns due to their association with severe storms, monsoons, and other meteorological phenomena. Additionally, cumulonimbus-induced lightning helps maintain the planet’s electrical balance while contributing to nitrogen fixation in the atmosphere.
What happens if you go through a cumulonimbus cloud?
Flying through a cumulonimbus cloud can be extremely dangerous for aircraft due to severe turbulence, hailstones, strong updrafts, and downdrafts that may cause sudden altitude changes or loss of control over the plane. Moreover, there is an increased risk of being struck by lightning, which could lead to electrical malfunctions or damage.
Are cumulonimbus clouds warm or cold?
Cumulonimbus clouds have both warm and cold sections within them depending on altitude levels: lower regions are typically warmer due to their proximity to Earth’s surface, while higher sections become progressively colder as they reach the tropopause. The temperature gradient within these clouds is a key factor in driving convection and storm development.
Conclusion
Cumulonimbus clouds are fascinating and powerful weather phenomena that can have a significant impact on our planet. In this article, we will explore the various factors that influence their formation, such as evaporation processes and the greenhouse effect.
We will also learn about lightning production in cumulonimbus clouds, mesoscale convective systems (MCSs), flash flood risks associated with these cloud formations, and how to differentiate them from other types of clouds. Finally, we will provide some online resources for further study on cumulonimbus clouds.
Cumulonimbus clouds are often referred to as thunderstorm clouds and for good reason. These clouds are capable of producing lightning, thunder, and heavy precipitation. They are formed through a process of convection, which involves the upward movement of warm, moist air. As this air rises, it cools and condenses, forming a cloud. If the conditions are right, the cloud will continue to grow and develop into a cumulonimbus cloud.
One of the key factors that influence the formation of cumulonimbus clouds is the amount of moisture in the air. When there is a lot of moisture present, the cloud is more likely to form and grow. This is why cumulonimbus clouds are often associated with humid tropical regions.
Another important factor is the amount of heat present in the atmosphere. When the air is warm, it is more likely to rise and form a cloud. This is why cumulonimbus clouds are often seen on hot summer days.
Lightning is a common occurrence in cumulonimbus clouds. This is because the cloud is made up of both positively and negatively charged particles. As the cloud grows and develops, these particles separate, creating an electrical charge. When the charge becomes strong enough, it is discharged as lightning.
Mesoscale convective systems (MCSs) are large clusters of thunderstorms that can form within cumulonimbus clouds. These systems can produce heavy rain, strong winds, and even tornadoes. They are most common in the summer months when the atmosphere is warm and humid.
Flash floods are another risk associated with cumulonimbus clouds. When these clouds produce heavy rain, it can quickly overwhelm drainage systems and cause flooding. It is important to be aware of the risks associated with these clouds and to take appropriate precautions.
To differentiate cumulonimbus clouds from other types of clouds, look for their distinctive shape. They are tall and vertical, with a flat top that resembles an anvil. They are often accompanied by thunder and lightning and can produce heavy rain and hail.
If you are interested in learning more about cumulonimbus clouds, there are many online resources available. The National Weather Service and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration both offer detailed information on these fascinating weather phenomena.
TimsWWW – Tim’s Wierd and Wonderful World Is A Blog About The Natural & Unnatural World