Summary of Key Points
- Sea Lamprey is an invasive species that poses a threat to native fish populations and the ecosystem.
- The sea lamprey has a natural range in the Atlantic Ocean but has been introduced to new waters through canals and shipping.
- The sea lamprey preys on native fish species, affecting the food web and ecosystem and causing economic impacts on the fishing industry.
- Control and management efforts include chemical methods, physical barriers, and research on biological control.
- There is a need for continued research and management efforts to prevent the spread of sea lamprey and minimize its impacts.
Introduction
The sea lamprey is a parasitic fish that has been causing problems in the Great Lakes region for over a century. This species was accidentally introduced to the Great Lakes through canals and shipping and has since become a major threat to the ecosystem and the fishing industry. In this article, we will uncover the threat posed by the species and explore the efforts being made to control and manage this invasive species.
Classification of the Sea Lamprey
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Subphylum: Vertebrata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Petromyzontiformes
- Family: Petromyzontidae
- Genus: Petromyzon
- Scientific Species Name: Petromyzon marinus
The Sea Lamprey is a parasitic fish that belongs to the Kingdom Animalia. It is a member of the Phylum Chordata and the Subphylum Vertebrata and is classified as a class Actinopterygii, meaning it has fins supported by bony rays. The sea lamprey belongs to the Order Petromyzontiformes, the Family Petromyzontidae, and the Genus Petromyzon. Its scientific species name is Petromyzon marinus.
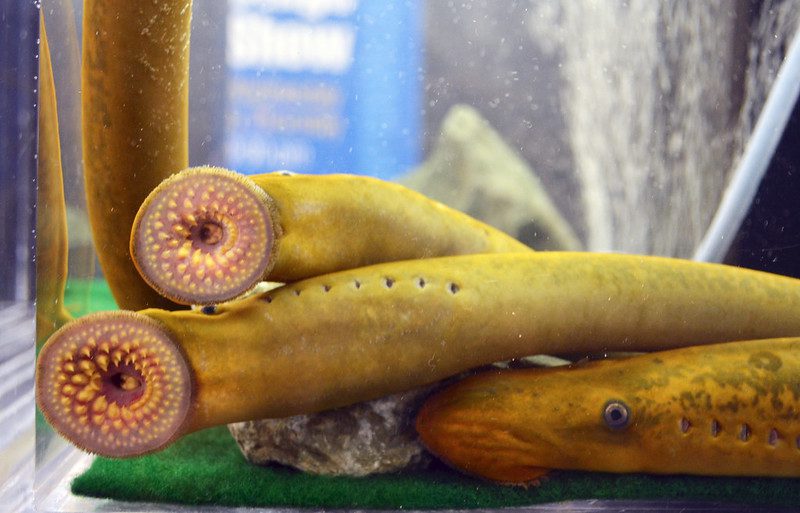

What is the Sea Lamprey
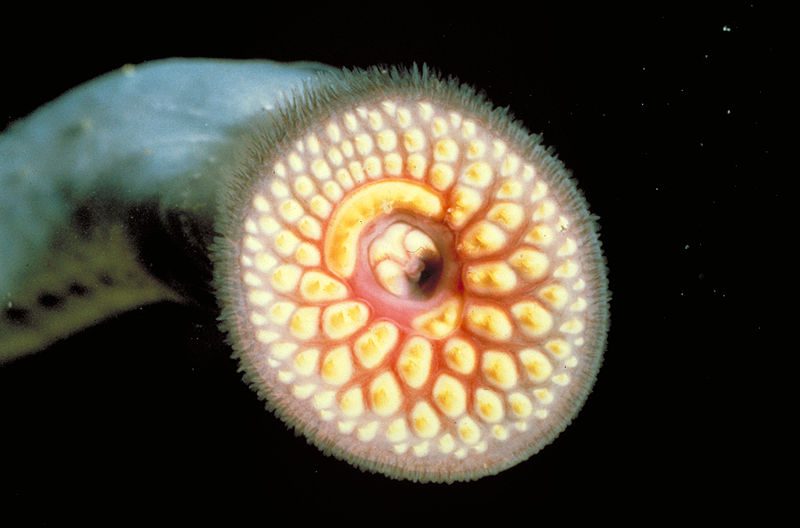
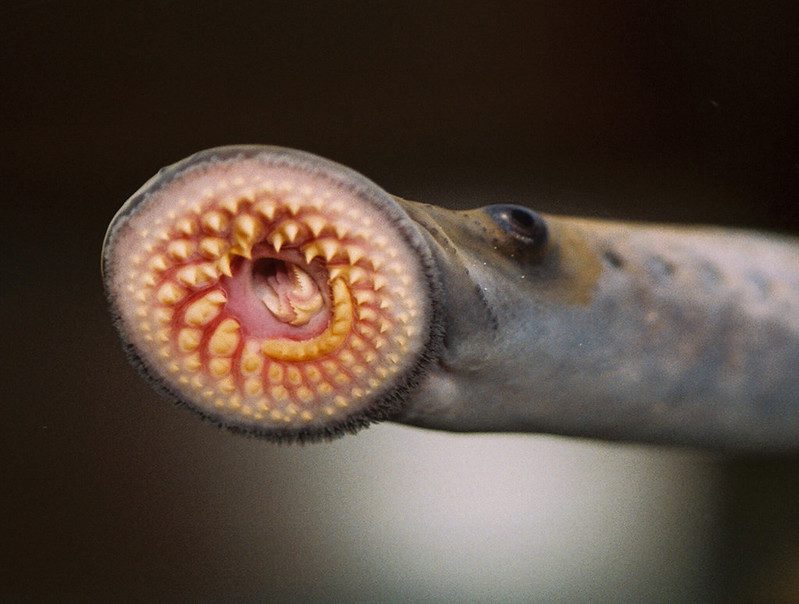
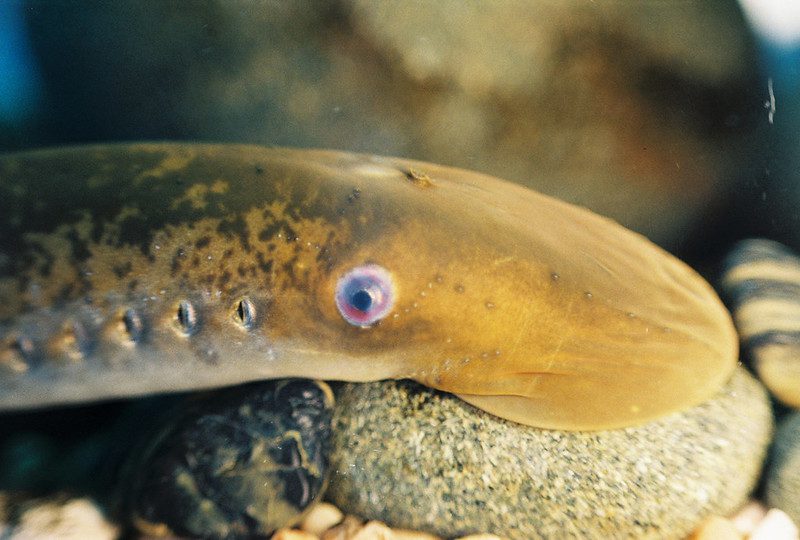
The sea lamprey is a type of parasitic fish that feeds on other fish’s blood and body fluids. It is characterized by its large, sucker-like mouth and sharp, teeth-like structures. This species is native to the Atlantic Ocean but has been introduced to new waters, including the Great Lakes region, through canals and shipping.
10 Facts about the Sea Lamprey
- Sea lampreys are parasitic fish that feed on other fish.
- They have a natural range in the Atlantic Ocean.
- They have been introduced to new waters, including the Great Lakes region.
- They have large, sucker-like mouths and sharp, teeth-like structures.
- They prey on native fish species, affecting the food web and ecosystem.
- The sea lamprey is responsible for economic impacts on the fishing industry.
- Control and management efforts include chemical methods, physical barriers, and research on biological control.
- They do not bite humans.
- They are not poisonous to humans.
- They do not hurt sharks.
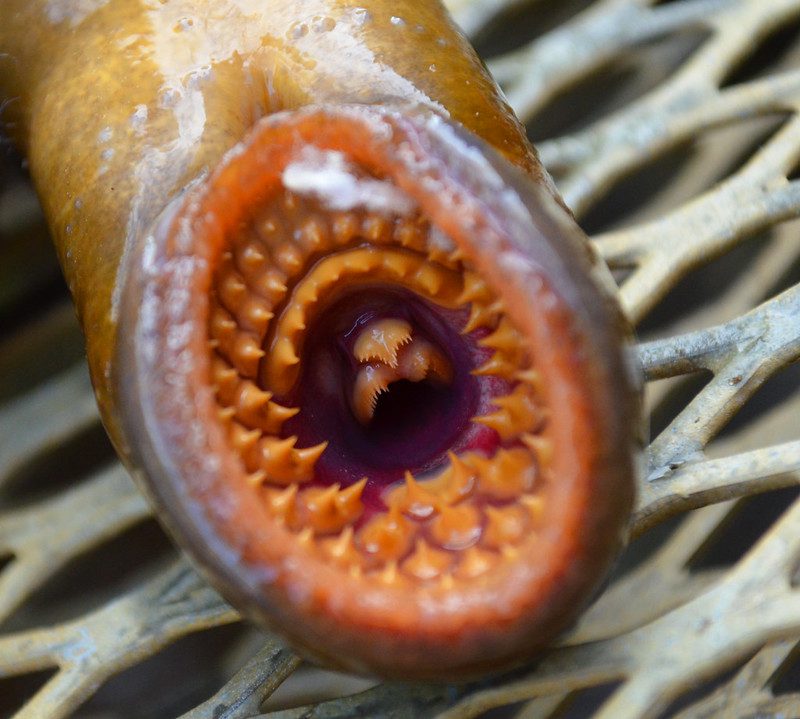

What Damage Does the Sea Lamprey Do?
It preys on native fish species, including lake trout and whitefish, causing significant declines in these populations. This affects the food web, ecosystem, and fishing industry, which relies on these species for commercial and recreational purposes.
Origin and Spread of Sea Lamprey
The sea lamprey has a natural range in the Atlantic Ocean but has been introduced to new waters through canals and shipping. The species was first discovered in the Great Lakes region in the late 1800s and has since spread throughout the system.
A Historical Timeline of the Sea Lamprey
- The 1830s – The sea lamprey is first observed in the Great Lakes region.
- The 1850s – The sea lamprey population in the Great Lakes region begins to cause significant declines in native fish populations.
- The 1900s – Chemical control methods, including pesticides, were developed to control sea lamprey populations.
- The 1930s – Physical barriers, such as dams and locks, are introduced to prevent sea lamprey migration to their spawning streams.
- The 1950s – The Great Lakes Fishery Commission is established to coordinate control and management efforts of the sea lamprey.
- The 1960s – The first sea lamprey control program is implemented using chemical and physical methods.
- The 1980s – Research on biological control begins, with the goal of developing a natural method of controlling sea lamprey populations.
- The 2000s – Ongoing control and management efforts continue, with a focus on improving and refining methods to prevent the spread of sea lamprey and minimize its impacts.
- Today – The sea lamprey remains a significant threat to the Great Lakes ecosystem and fishing industry, and efforts to control and manage this invasive species continue.
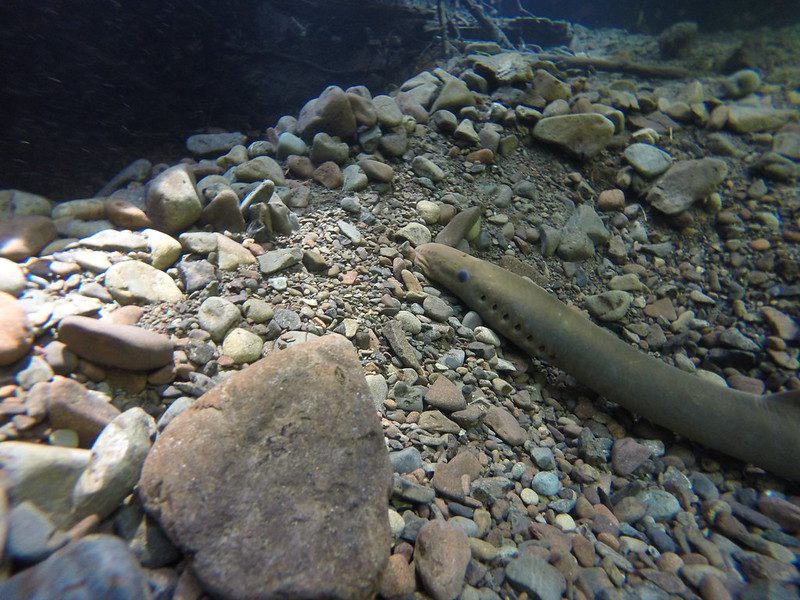

The Natural Range of Sea Lamprey
The sea lamprey is native to the Atlantic Ocean and is found along the coast from Labrador to Florida.
Historical Introduction to New Waters
The sea lamprey was introduced to new waters through canals and shipping. The species was first discovered in the Great Lakes region in the late 1800s and has since spread throughout the system.
The Current Distribution of Sea Lamprey
Today, the sea lamprey is found in the Atlantic, eastern North Atlantic, Baltic, Adriatic, and Mediterranean seas and throughout the Great Lakes region and has been responsible for significant declines in native fish populations.
Reproduction of Sea Lamprey
The sea lamprey reproduces by laying its eggs in freshwater streams, where the larvae develop before migrating to the ocean to mature. The mature sea lampreys then return to freshwater streams to feed on native fish species.
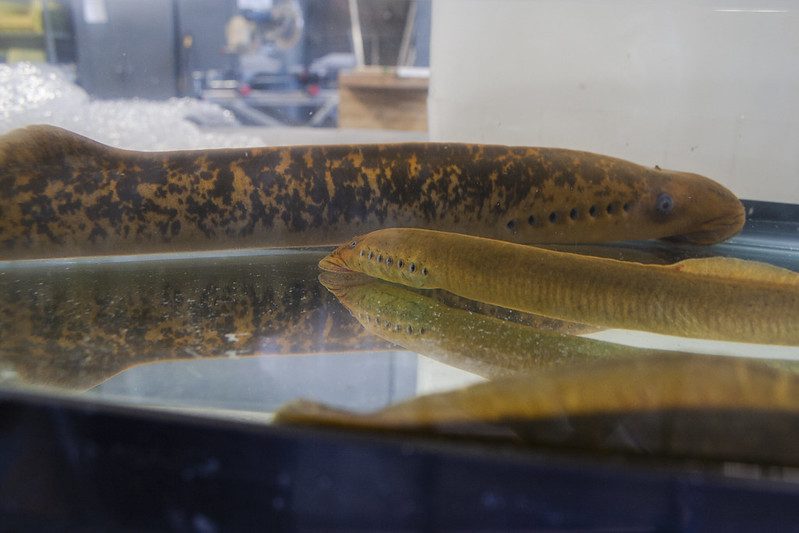

Ecological Impacts of Sea Lamprey
The sea lamprey preys on native fish species, including lake trout and whitefish, causing significant declines in these populations. This affects the food web, ecosystem, and fishing industry, which relies on these species for commercial and recreational purposes.
Predation on Native Fish Species
The sea lamprey preys on native fish species, causing significant population declines. This affects the food web, ecosystem, and fishing industry, which relies on these species for commercial and recreational purposes.
Effect on Food Web and Ecosystem
The decline in native fish populations caused by the sea lamprey affects the food web and ecosystem, leading to imbalances and potential long-term consequences.

Economic Impacts on the Fishing Industry
The sea lamprey has caused economic impacts on the fishing industry, as the decline in native fish populations has reduced the availability of commercially and recreationally important species.
Control and Management Efforts
Control and management efforts to prevent the spread of sea lamprey and minimize its impacts include chemical methods, physical barriers, and research on biological control.
Chemical Control Methods
Chemical control methods involve the use of chemicals to kill or sterilize the fish in their spawning streams. This method has effectively reduced sea lamprey populations but also has potential negative impacts on the environment and non-target species.
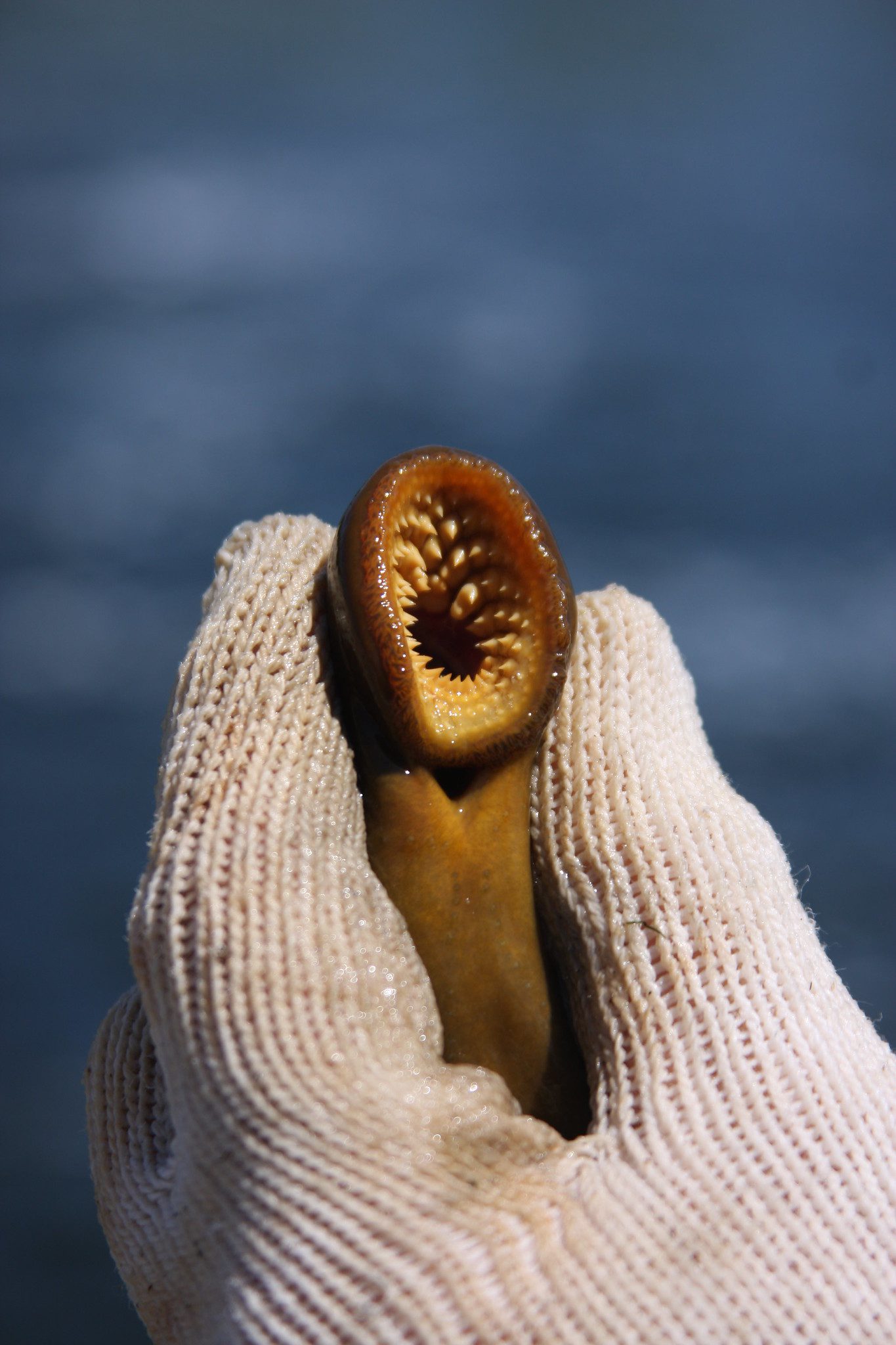

Physical Barriers and Barriers to Migration
Physical barriers, such as dams and locks, can be used to prevent sea lampreys from reaching their spawning streams. This method has effectively reduced sea lamprey populations but also has potential negative impacts on other species and the ecosystem.
Research on Biological Control
Research on biological control involves the study of natural predators and parasites of sea lampreys, with the goal of developing a natural method of control. This method has the potential as a long-term solution, but more research is needed to understand its effects and potential impacts fully.

Discussion of Future Prospects for Control and Management of Sea Lamprey
The future prospects for control and management of sea lamprey depend on continued efforts to prevent the spread of this invasive species and minimize its impacts. Chemical and physical control methods have been effective, but there is a need for continued research on biological control and long-term solutions.
Call to Action for Continued Research and Management Efforts
Continued research and management efforts need to prevent the spread of sea lamprey and minimize its impacts. This includes further study of chemical and physical control methods and research on biological control and long-term solutions.

People Also Ask
Do Sea Lamprey Bite Humans?
No, sea lampreys do not bite humans.
Is Sea Lamprey Poisonous?
No, sea lampreys are not poisonous to humans.
Do Lampreys Hurt Sharks?
No, lampreys do not hurt sharks.
What Happens if a Lamprey Bites You?
Lampreys do not bite humans, so there is no risk of being bitten by a lamprey.
Do Humans eat Lampreys?
Lampreys were once a traditional food source for indigenous peoples but are not widely consumed by humans today.
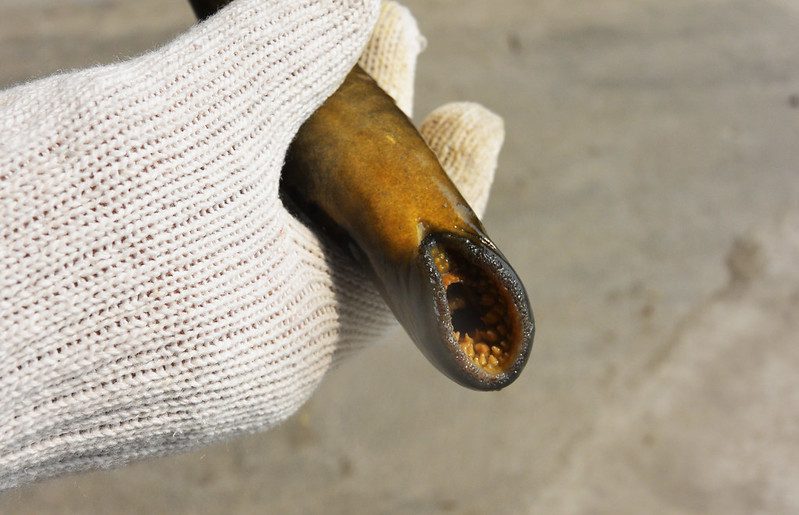

What if You Fell into a Pool of Lampreys:
Falling into a pool of lampreys would not be harmful to a human, as lampreys do not bite or attack humans. However, it would likely be an uncomfortable and potentially slippery situation.
What Eats Sea Lamprey
Sea lampreys have natural predators, including larger fish species, birds, and other predatory animals. Humans also control and manage them through chemical, physical, and biological methods.