Introduction To The Australian Green Tree Frog
The Australian Green Tree Frog is a small to medium-sized frog native to Australia and New Guinea. It is also known as the Dumpy Tree Frog or Green Frog due to its bright green skin. This species is widely distributed throughout eastern and northern Australia, making it a familiar sight in many areas.
Classification
- Scientific species name: Litoria caerulea
- Genus: Litoria
- Class: Amphibia
- Family: Hylidae
- Order: Anura
- Subphylum: Vertebrata
- Phylum: Chordata
- Kingdom: Animalia
The Australian green tree frog (Litoria caerulea) is an amphibian species belonging to the family Hylidae, a group of tree frogs found in the Americas, Europe, and Asia.
This species is classified in the genus Litoria and is a member of the class Amphibia, which includes frogs, toads, and salamanders.
The class Amphibia is part of the subphylum Vertebrata, which includes animals with backbones, and the phylum Chordata, which includes all animals with a spinal cord. The Australian green tree frog is classified in the kingdom Animalia, which includes all animals.
11 Australian Green Tree Frog Facts
- Australian green tree frogs are native to eastern and northern Australia and parts of New Guinea.
- They are a type of tree frog known for their bright green color, which can vary in intensity depending on their surroundings and mood.
- These frogs can reach up to 10 cm in length and have smooth, moist skin that helps them absorb water and nutrients.
- Australian green tree frogs are primarily nocturnal, spending their days hiding in trees, bushes, and other vegetation.
- They can vocalize, and their calls sound like a series of short, high-pitched “quacks.”
- These frogs can absorb water and oxygen through their skin, allowing them to survive for long periods without access to water or air.
- They are carnivorous and feed on insects, spiders, and other small invertebrates.
- Australian green tree frogs are highly adaptable and can be found in a variety of habitats, including rainforests, wetlands, and suburban gardens.
- They are popular pets in Australia and around the world due to their easy care requirements and docile nature.
- Australian green tree frogs are not endangered but are protected in some parts of their range due to habitat loss and other threats.
Physical Characteristics
The Australian Green Tree Frog has an average size of 7-10 cm (2.8-3.9 in) and is known for its bright green color. However, it can also be found in shades of blue or yellow. Its skin is smooth with small bumps called tubercles, and it has large eyes with horizontal pupils. The Australian Green Tree Frog’s webbed toes help it climb trees and other structures.
Green Tree Frog Distribution and habitat
Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea) are native to Australia and New Guinea and are widely distributed throughout eastern and northern Australia. These frogs are found in a variety of habitats, including rainforests, wetlands, and gardens, and they are able to adapt to a range of different environments.
Green tree frogs are most commonly found in areas with plenty of moisture, as they require water to survive. They are often found near ponds, streams, and other bodies of water, and they are particularly fond of rainforests and other humid environments.
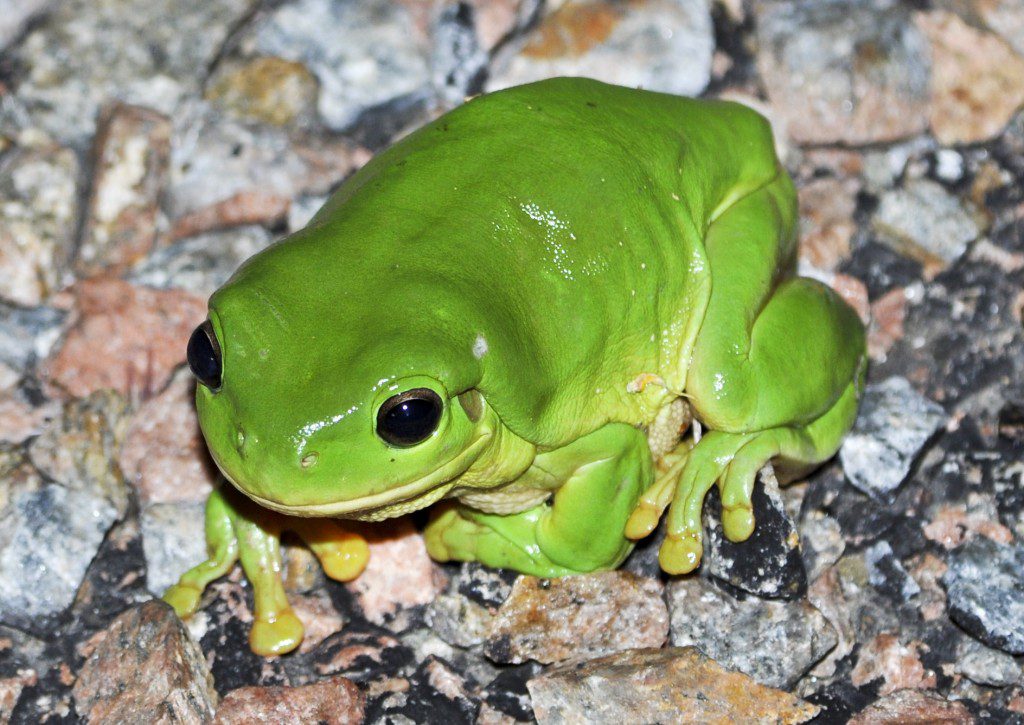

In addition to their preference for moist habitats, green tree frogs are also attracted to areas with a reliable food supply. These frogs feed on a variety of insects and other small invertebrates, and they are attracted to areas where these prey are abundant.
Green tree frogs are also attracted to gardens and other areas with a reliable source of water, as these environments provide both food and moisture.
Overall, the distribution and habitat of the Australian green tree frog are wide-ranging and varied, and these frogs are able to adapt to a range of different environments. Whether in rainforests, wetlands, or gardens, Australian green tree frogs are able to find the resources they need to survive and thrive.
The Australian Green Tree Frog can be found in a variety of habitats, including rainforests, wetlands, and gardens. It prefers to live in trees but will also inhabit burrows or other ground-level hiding spots.
This species is widely distributed throughout eastern and northern Australia, including Queensland, New South Wales, and the Northern Territory.
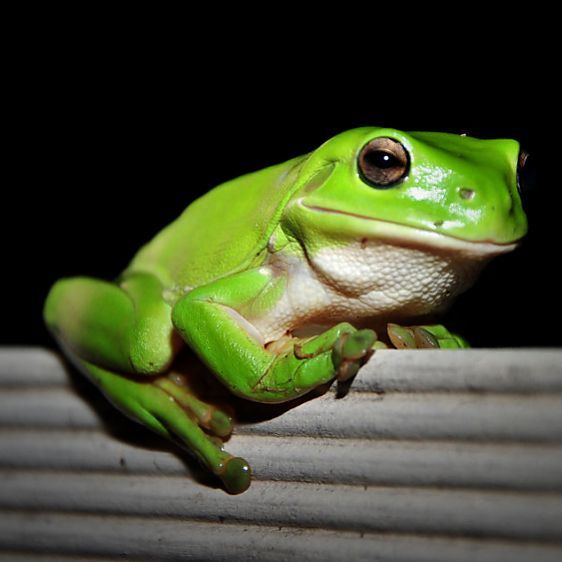

Behavior and Diet
The Australian Green Tree Frog is nocturnal, meaning it is most active at night. It is known for its distinctive “quack” call, which it uses to communicate with other frogs. The diet of the Australian Green Tree Frog consists primarily of insects, spiders, and other small invertebrates.
Reproduction
The Australian Green Tree Frog breeds during the wet season, typically from October to March. Male frogs use calls to attract females, who lay eggs in clumps on the surface of water bodies. These eggs hatch into tadpoles, which eventually metamorphose into adult frogs.
Conservation Status
The Australian Green Tree Frog is not currently listed as threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). However, populations of this species may be declining in some areas due to habitat loss and the impacts of climate change. It is important to protect the habitat of this and other frog species to ensure their continued survival.
Green Tree Frog Call
The Australian Green Tree Frog (Litoria caerulea) is known for its distinctive “quack” call, which it uses to communicate with other frogs. This call is most often heard at night when the frog is most active. The call of the male Australian Green Tree Frog is slightly higher pitched and more frequent than that of the female.
In addition to the “quack” call, the Australian Green Tree Frog can make various other sounds. These can include chirping, trilling, and croaking sounds. Scientists and naturalists often use the calls of the Australian Green Tree Frog to locate and identify this species in the wild.
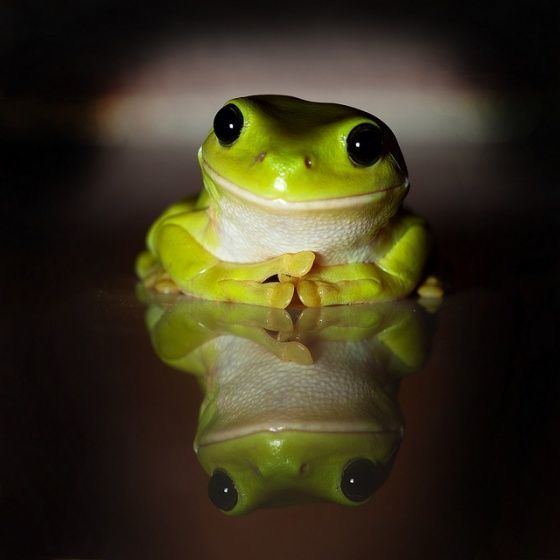

Despite its small size, the Australian Green Tree Frog has a powerful voice that can be heard over long distances. Its calls are an important part of the nighttime soundscape in many parts of Australia and New Guinea. So, if you’re ever out in the wild at night and hear a distinctive “quack” sound, you might be in the presence of an Australian Green Tree Frog!
Are Australian green tree frogs poisonous to humans?
No, Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea) are not poisonous to humans. These frogs are not toxic and do not produce any toxins that can harm humans. They are generally considered safe to handle and are not a threat to humans.
While Australian green tree frogs are not poisonous to humans, it is still important to handle them with care. Like all wild animals, they may carry diseases or parasites that can be transmitted to humans. It is always a good idea to wash your hands after handling any wild animal, including frogs.
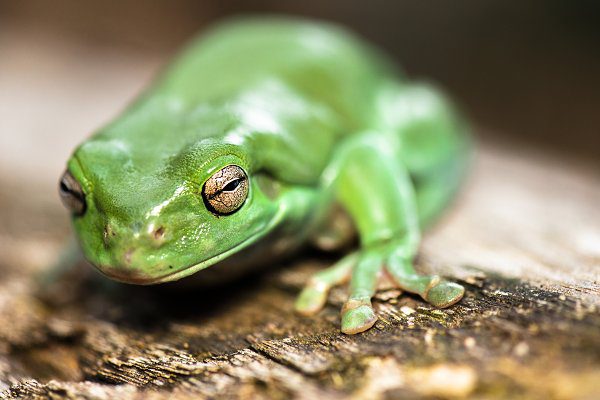

In addition, it is important to remember that all wild animals, including frogs, should be treated with respect and left in their natural habitat. It is illegal to capture or keep Australian green tree frogs as pets without a special permit, and it is important to protect these and other wild species for the benefit of future generations.
Can you touch a green tree frog?
It is generally safe to handle Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea), as they are not poisonous or toxic to humans. However, it is important to handle these frogs with care and to follow some basic guidelines to minimize any stress on the animal and reduce the risk of transmission of diseases or parasites.
If you choose to handle an Australian green tree frog, wash your hands before and after handling the animal. This will help reduce the risk of transmitting diseases or parasites the frog may carry. It is also important to handle the frog gently and to avoid squeezing or applying too much pressure to its body.
It is important to remember that all wild animals, including frogs, should be treated with respect and left in their natural habitat whenever possible. It is illegal to capture or keep Australian green tree frogs as pets without a special permit, and it is important to protect these and other wild species for the benefit of future generations.
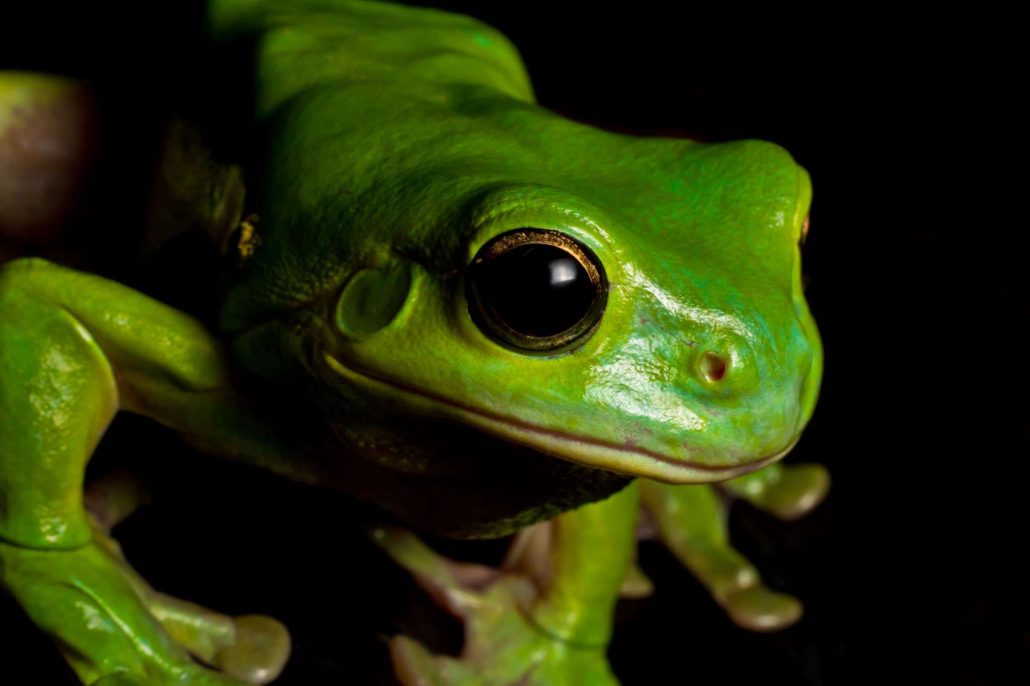

What eats a green tree frog?
Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea) are preyed upon by a variety of animals, including snakes, birds, and mammals. In their natural habitat, they may be eaten by predators such as goannas, snakes, and large birds of prey such as owls and eagles.
In urban areas, Australian green tree frogs may be preyed upon by domestic cats and dogs and introduced species such as rats and foxes. These frogs are also vulnerable to habitat destruction, which can limit their access to food and shelter and make them more vulnerable to predation.
Despite the many predators that may prey on Australian green tree frogs, these animals have a number of adaptations that help them to survive in the wild.
These adaptations include bright coloring, which may help them to blend in with their surroundings and avoid being noticed by predators, and the ability to climb trees and other structures, which allows them to escape from danger.
Overall, Australian green tree frogs are able to successfully evade predators and reproduce, ensuring the continued survival of their species.
How can you tell if a green tree frog is male or female?
It can be difficult to determine the gender of Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea) based on physical characteristics alone, as males and females are generally similar in size and appearance. However, there are a few subtle differences that can help to distinguish males from females.
One way to determine the gender of an Australian green tree frog is to listen for its call. Male frogs tend to have higher-pitched calls that are more frequent than those of females. The calls of male frogs are often used to attract females during the breeding season.

Another way to distinguish males from females is to look for physical characteristics such as the size and shape of the thumb pads. Male frogs tend to have larger thumb pads, which are used to help hold onto females during mating. However, these differences can be subtle and may not be visible to the naked eye.
In general, the most reliable way to determine the gender of an Australian green tree frog is to have it examined by a trained professional, such as a veterinarian or a herpetologist (a specialist in reptiles and amphibians). These individuals are trained to identify the gender of frogs based on a variety of physical characteristics.
Do green tree frogs like to be held?
It is generally not recommended to hold Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea) for prolonged periods of time, as this can be stressful for the animal and may cause it to become agitated. These frogs are wild animals and are not used to being handled by humans, so it is important to handle them with care and to minimize any stress or discomfort to the animal.
If you choose to handle an Australian green tree frog, it is important to do so gently and avoid squeezing or applying too much pressure to its body. It is also a good idea to wash your hands before and after handling the frog, as this can help to reduce the risk of transmitting any diseases or parasites that the frog may carry.
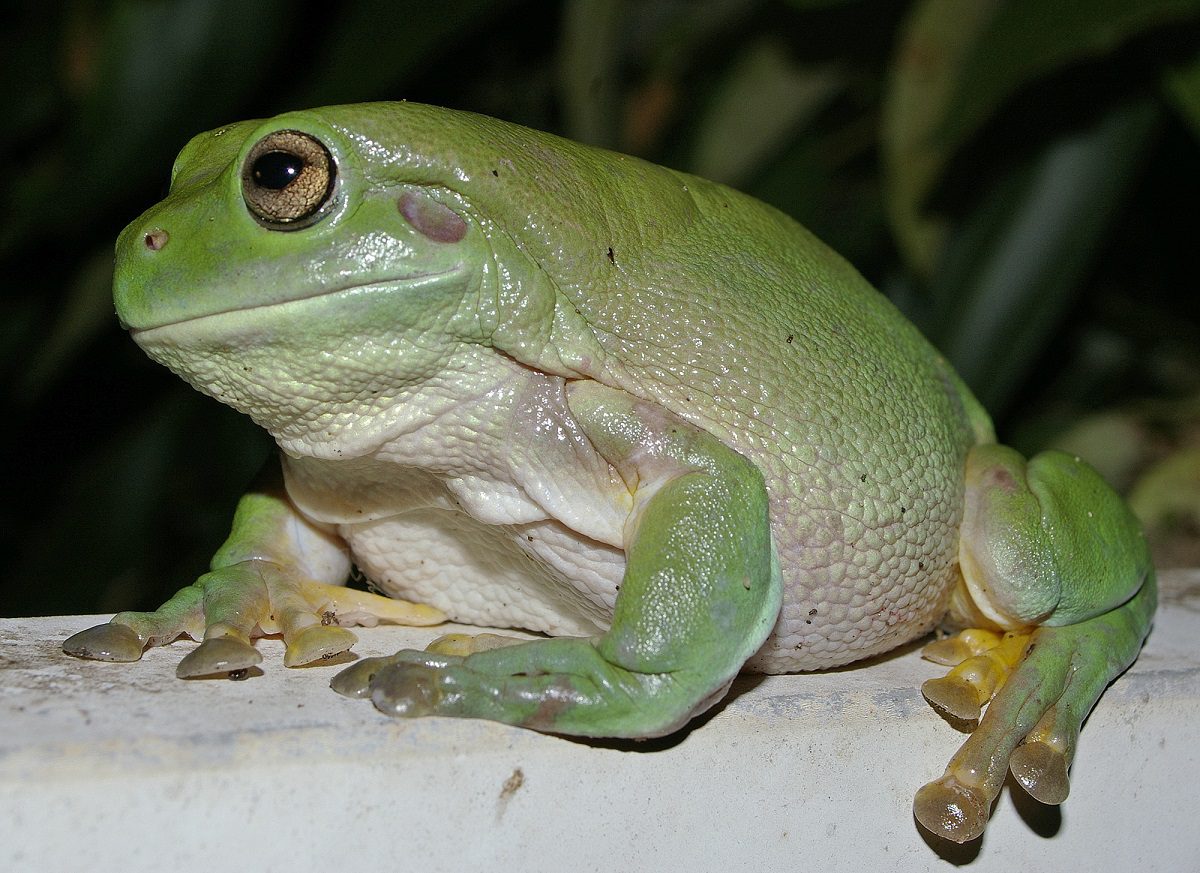

Overall, it is best to observe Australian green tree frogs in their natural habitat and allow them to do business without interference. These frogs are fascinating and important members of the ecosystem, and it is important to respect their wildness and to leave them in their natural habitat whenever possible.
What attracts green tree frogs?
Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea) are attracted to a variety of factors, including food sources, water, and suitable breeding sites. These frogs are most active at night and use their calls to communicate with other frogs and attract potential mates.
During the breeding season, male green tree frogs use calls to attract females, who are attracted to the sound of the male’s call. Once a female has chosen a mate, the male will use his thumb pads to hold onto the female during mating.
In terms of habitat, green tree frogs are attracted to areas with plenty of moisture, as they require water to survive. They are often found near ponds, streams, and other bodies of water, and they are particularly fond of rainforests and other humid environments.
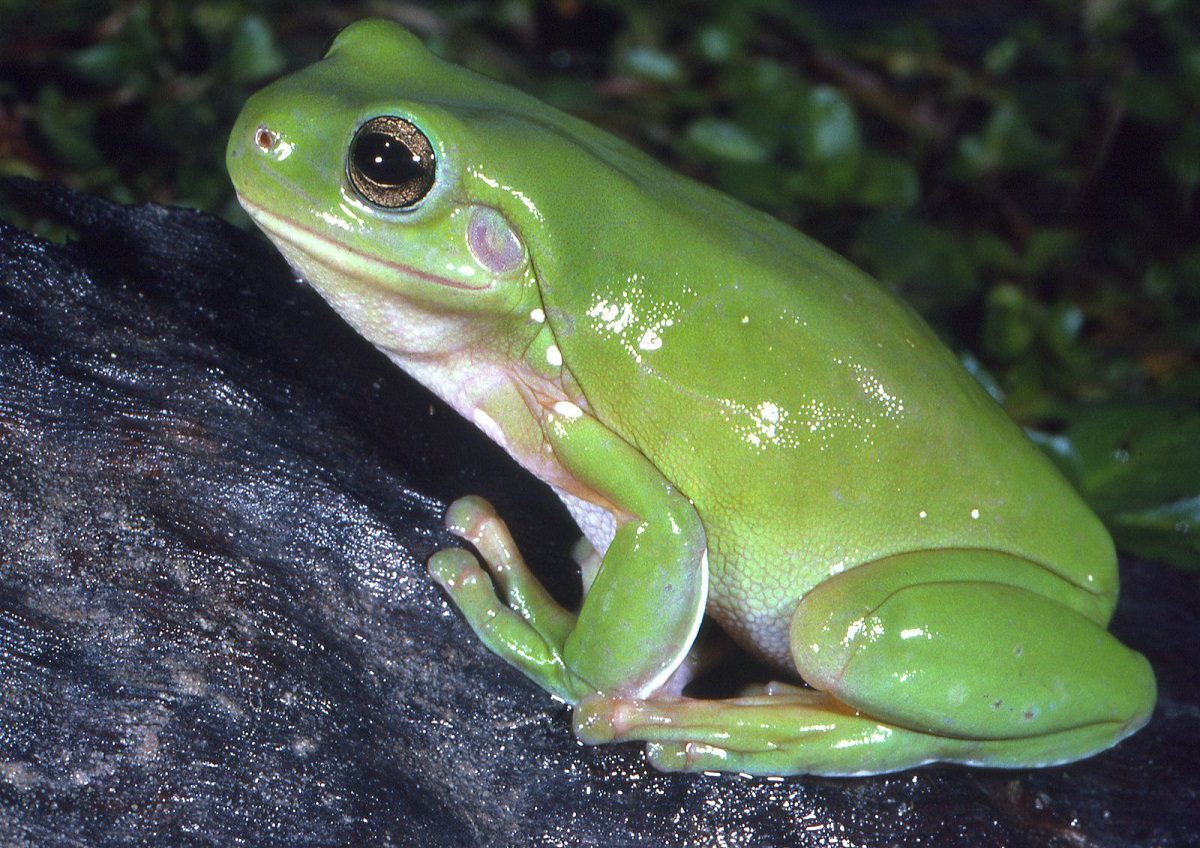

Food is also an important factor in attracting green tree frogs. These frogs feed on a variety of insects and other small invertebrates, and they are attracted to areas where these prey are abundant.
Green tree frogs are also attracted to gardens and other areas with reliable water sources, as these environments provide both food and moisture. Overall, green tree frogs are attracted to environments that provide the resources they need to survive and reproduce.
What do green tree frogs eat In Australia?
Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea) are carnivorous and feed on a variety of insects and other small invertebrates. These frogs are opportunistic feeders and will eat a wide range of prey, including flies, mosquitoes, beetles, moths, and spiders.
In addition to insects, green tree frogs may also feed on other small animals, such as snails and worms. They are known to be attracted to lights at night, and they may be found feeding on insects that are attracted to porch lights or other artificial light sources.
Green tree frogs are most active at night and do most of their hunting and feeding during this time. They use their long, sticky tongues to capture prey, and they are able to consume a variety of different types of food thanks to their adaptable digestive systems.
Overall, the diet of the Australian green tree frog is diverse and varied, and it is well-suited to the many different habitats in which these frogs can be found. Whether in rainforests, wetlands, or gardens, Australian green tree frogs are able to find the food they need to survive and thrive.
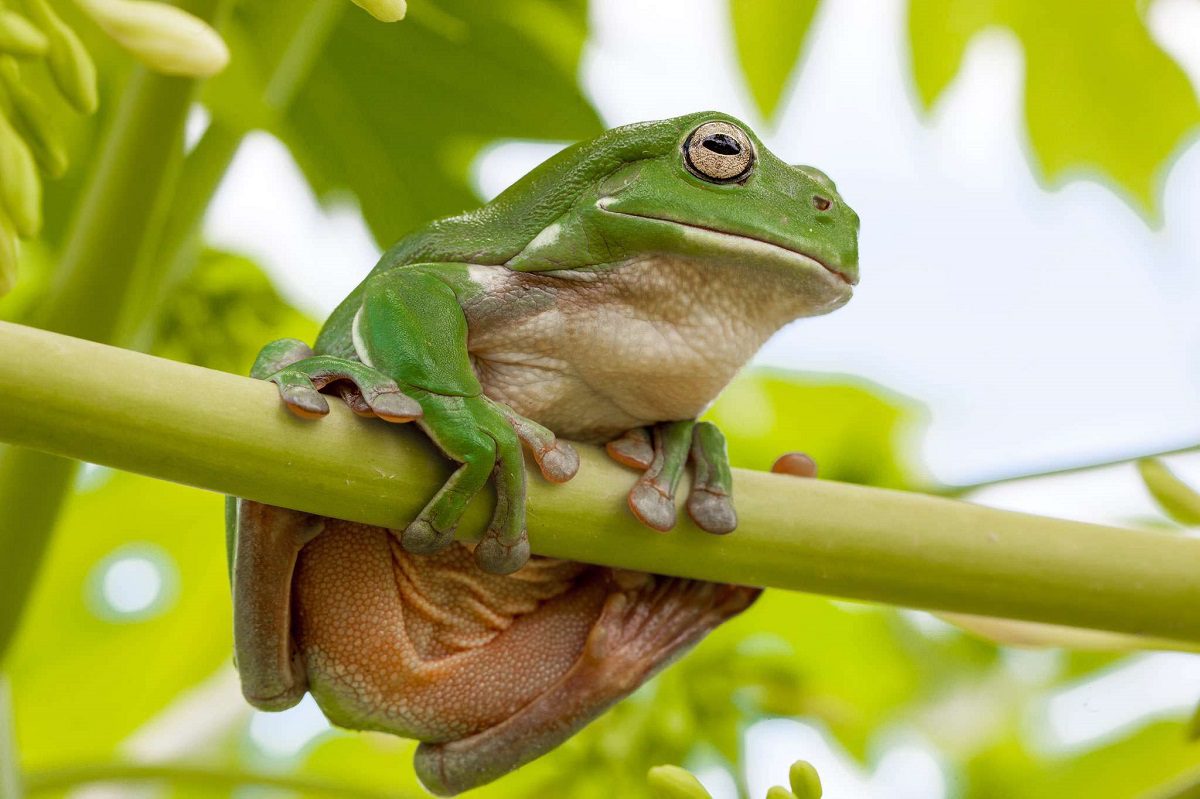

How many green tree frogs can live together?
Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea) are social animals and are often found in large groups, especially during the breeding season. In general, these frogs are not aggressive toward one another and are able to coexist peacefully in large numbers.
During the breeding season, it is not uncommon for large groups of green tree frogs to gather at breeding sites, such as ponds or streams. These frogs may use their calls to attract potential mates and to establish territories.
In terms of long-term cohabitation, it is not clear how many green tree frogs can live together in a single enclosure. These frogs are generally tolerant of one another and do not usually exhibit aggressive behavior, but it is important to provide them with adequate space and resources to ensure their well-being.
In general, it is best to consult with a veterinarian or a herpetologist (a specialist in reptiles and amphibians) if you are considering keeping green tree frogs as pets. These professionals can provide guidance on the appropriate number of frogs to keep in a single enclosure and can help to ensure that the frogs have the resources they need to thrive. Overall, green tree frogs are social animals that are able to coexist peacefully in large groups.

Australian Green Tree Frog Tadpoles & Reproduction

Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea) reproduce during the wet season, which typically runs from October to March in their native range. During this time, male frogs use calls to attract females, who lay eggs in clumps on the surface of water bodies.
The eggs of the Australian green tree frog hatch into tadpoles, which are small, aquatic larvae with long tails and tiny, developing legs. The tadpoles of the Australian green tree frog are typically brown or green in color and have a streamlined body shape that is well-suited to swimming.
Tadpoles are herbivorous, and they feed on algae and other aquatic plants. They grow quickly and undergo a process of metamorphosis, during which they develop legs and other adult characteristics. This process typically takes several months to complete, and once it is finished, the tadpoles emerge from the water as fully-formed green tree frogs.
Australian green tree frogs are an important part of the ecosystem, and their reproduction plays a vital role in the survival of their species. It is important to protect the habitats of these and other frog species to ensure their continued survival and success.
Overall, the reproduction of Australian green tree frogs involves a complex and fascinating process that begins with the laying of eggs and ends with the emergence of adult frogs.
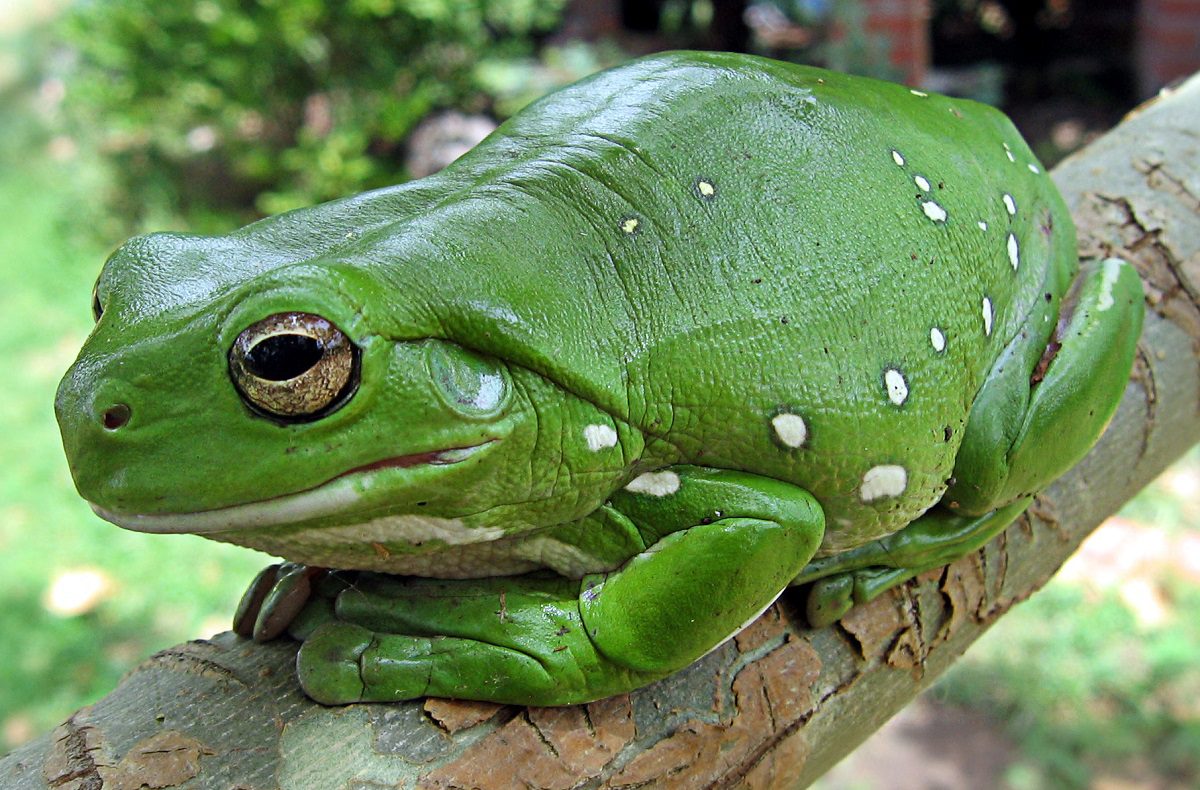

Green Tree Frog As Pets
Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea) can make interesting and entertaining pets for those who are willing to provide them with the proper care and attention. However, it is important to remember that these frogs are wild animals, not domesticated. As such, they have specific care needs and may not be suitable for everyone.
Before considering an Australian green tree frog as a pet, it is important to research the specific care requirements of this species and to ensure that you are able to provide for all of its needs.
Green tree frogs require a spacious enclosure with plenty of hiding spots, as well as a source of water and a varied diet of insects and other small invertebrates. They also require a consistent temperature and humidity level and should be kept in an environment that mimics their natural habitat as closely as possible.
It is also important to remember that it is illegal to capture or keep Australian green tree frogs as pets without a special permit. Suppose you are interested in keeping an Australian green tree frog as a pet. In that case, purchasing one from a reputable breeder or adopting one from a rescue organization is recommended.
How to apply for a Native Animal Keeping Licence
If you are interested in keeping native Australian animals, including Australian green tree frogs (Litoria caerulea), as pets, you may need to apply for a Native Animal Keeping Licence (NAKL). This license is issued by the relevant state or territory government agency and allows you to keep certain native species as pets.
To apply for a Native Animal Keeping Licence, you will need to contact the relevant government agency and complete the necessary application process. This process typically involves filling out an application form and providing required documentation, such as proof of identity and address. You may also need to pay a fee to apply for the license.
In addition to the application process, you must meet certain requirements to be eligible for a Native Animal Keeping Licence. These requirements may vary depending on the state or territory in which you live, but they may include:
- Having suitable housing and enclosures for the animal
- Having the necessary knowledge and experience to care for the animal
- Having a suitable diet and feeding plan for the animal
- Having a plan in place to deal with any emergencies or unexpected events
If you are granted a Native Animal Keeping Licence, you will be responsible for ensuring that the animal is well-cared for and that all of its needs are met. This may include providing the animal with appropriate housing, food, and medical care and ensuring that it is not subjected to any unnecessary stress or discomfort.
Overall, obtaining a Native Animal Keeping Licence is an important step in the process of keeping native Australian animals as pets, and it is important to follow the necessary procedures and meet the required criteria to ensure that the animal is well-cared for and protected.
You can apply for a Native Animal Keep License here
Overall, Australian green tree frogs can make interesting and rewarding pets for those who are able to provide them with the proper care and attention. However, it is important to carefully consider whether these frogs are the right choice for you and to do your research to ensure that you are able to provide for all of their needs.