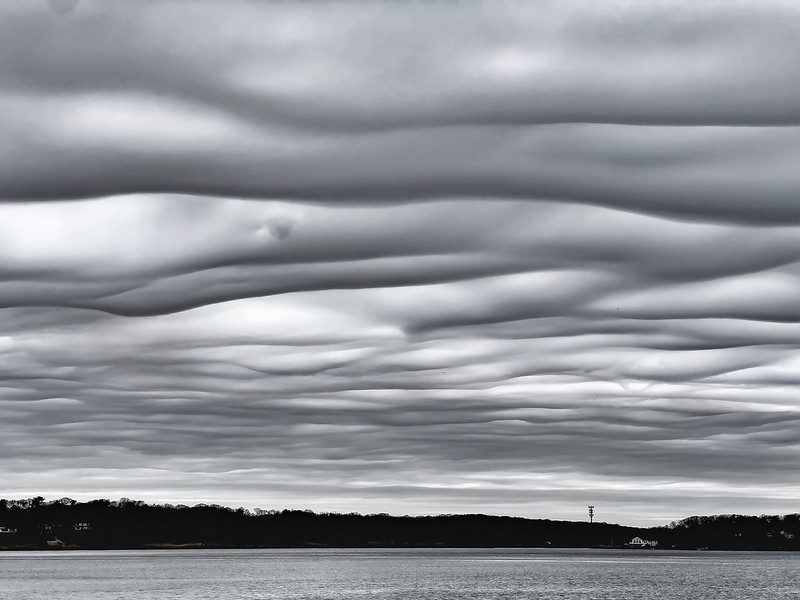
Picture this: you’re gazing at the sky when suddenly, a breathtaking formation of rare Asperitas clouds appears above you.
These mesmerizing cloud formations resemble rippling ocean waves and have captured the attention of meteorologists and enthusiasts alike. In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the world of Asperitas clouds, exploring their unique characteristics and uncovering the secrets behind their formation.
We’ll discuss how citizen science played a crucial role in discovering these captivating cloud structures and celebrate their official recognition by the World Meteorological Organization. Furthermore, we will delve into various factors that contribute to their development, such as orography, wind shear, convection currents, and atmospheric gravity waves.
Intrigued? Join us on this journey through the skies as we unravel one of nature’s most fascinating phenomena – rare Asperitas clouds.
Asperitas Clouds – A Rare Phenomenon
Gaze skyward and behold a captivating cloud formation, one that appears to be taken from the pages of an intergalactic adventure.
Welcome to the world of Asperitas clouds, also known as Undulatus Asperatus.
In 2017, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) acknowledged these uncommon wonders as the first new clouds to be added to their atlas in nearly 70 years.
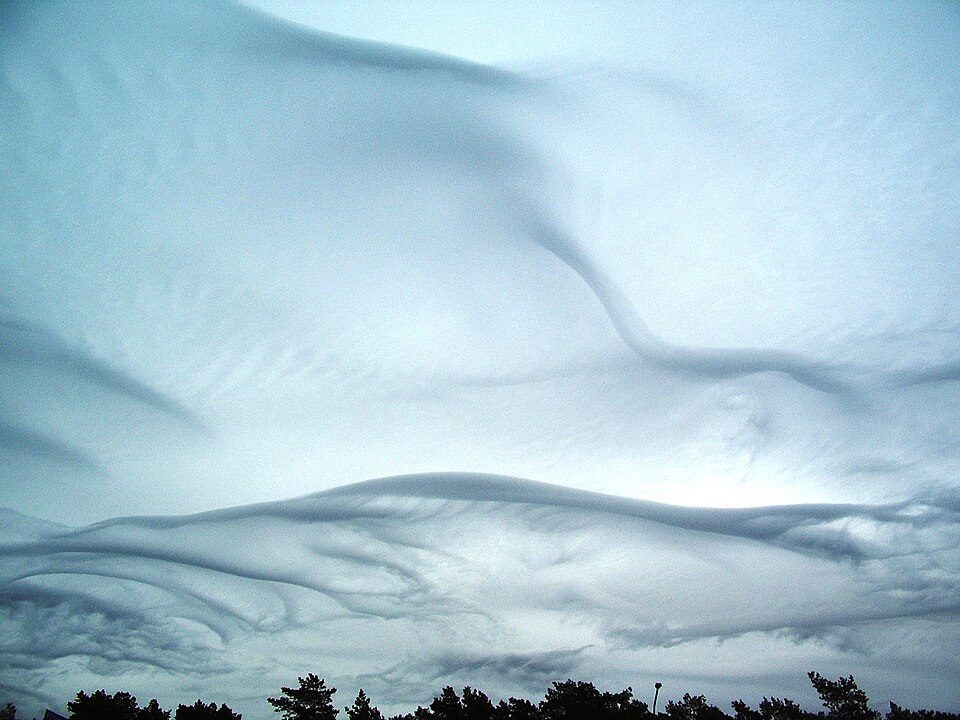

Discovery of Asperitas Clouds through Citizen Science
The discovery of these fascinating formations is largely thanks to citizen scientists who captured their unique appearance on camera and shared it with researchers.
This collaborative effort led to an increased understanding of these elusive clouds and ultimately resulted in their official recognition by experts.
Official Recognition by the World Meteorological Organization
In 2017, after much research and deliberation, WMO added Asperitas clouds into its International Cloud Atlas – a significant milestone for both amateur hobbyists and professional meteorologists alike.
So, what makes Asperitas clouds so special?
Their unique appearance is characterized by highly developed structures at their base due to wind and temperature changes, creating a rough texture that indicates unusual instability.
But don’t be fooled – despite their ominous look, they typically do not result in precipitation like other similar-looking formations such as Mammatus or Kelvin-Helmholtz waves.
Intrigued by these rare wonders of nature?
Dive deeper into our blog to learn more about the formation process, the potential causes behind them, and how gravity waves may play a role in shaping these mesmerizing clouds.
Cloud Formation and Types: A Quick Guide
Let’s talk about clouds.
Have you ever wondered how these fluffy wonders form in the sky? Well, buckle up because we’re about to embark on a cloud-formation journey.
Ready? Let’s go.
The Process of Cloud Formation
The secret ingredient for cloud formation is saturated air reaching its dew point.
This occurs when water vapor condenses into liquid due to cooling air or increased saturation from an adjacent water source.
Primary Cloud Types
Cloud enthusiasts rejoice. There are five primary types of clouds you can spot in the skies:
- Stratus: These low-level clouds appear as flat layers covering large areas. Think gloomy days with gray skies.
- Cumulus: The classic cotton candy-like puffs that make you want to reach out and grab them. They usually indicate fair weather conditions.
- Stratocumulus: When stratus and cumulus merge, they create this hybrid – low-level clumps or rolls that cover parts of the sky.
- Cumulonimbus: Towering giants responsible for thunderstorms, heavy rain, hail, and even tornadoes. Approach with caution.
- Cirrus: High-altitude wispy formations made mostly of ice crystals – often seen as harbingers of changing weather patterns.

But wait, there’s more.
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Cloud Atlas also includes accessory clouds and supplementary features to further classify these fascinating formations.
And speaking of fascinating formations, have you heard of the rare Asperitas clouds? These clouds, recognized by the Cloud Appreciation Society, resembled rippling ocean waves and were officially added to the International Cloud Atlas in 2017 as undulatus asperatus.
So next time you’re cloud-gazing, impress your friends with your newfound knowledge of the sky’s natural wonders.
Characteristics of Asperitas Clouds
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of Asperitas clouds, shall we?
These rare beauties are not your average low-elevation layered clouds. Their highly developed structures at the base make them stand out from the crowd, thanks to wind and temperature changes. Asperitas clouds, also known as Undulatus Asperatus, have a rough appearance that indicates unusual instability at their base layer.
But wait, there’s more. Rather than resulting in precipitation like other similar-looking formations, such as Mammatus or Kelvin-Helmholtz waves, these intriguing cloud formations remain dry.
Low Elevation Layered Structure
You’ll find Asperitas clouds closer to Earth’s surface compared to some other cloud types. This is because they form within the lower atmosphere, where air currents can create those captivating wavy patterns resembling rippling ocean waves on a stormy day.
Highly Developed Bottom Structures
The magic happens at the bottom of these unique cloud formations. The Cloud Appreciation Society explains that the undulating patterns at their base are created by varying wind speeds and temperature changes within different layers of the atmosphere. This results in a stunning display of atmospheric artistry.
Unusual Instability at Base Layer
Asperitas clouds have an air of mystery surrounding them, as their cause for instability is still unknown. However, this enigmatic quality only adds to their allure and keeps researchers on their toes. The World Meteorological Organisation added these rare cloud formations to its International Cloud Atlas in 2017 and continues to investigate what causes this unusual turbulence.
Potential Causes for Asperitas Cloud Formation
Alright, let’s dive into the mysterious world of Asperitas clouds.
These fascinating formations have left researchers scratching their heads and proposing several potential causes. We’ll explore some of these theories below:
Orography and Terrain Effects
One possibility is that orography, or the effect of terrain on weather patterns, plays a role in shaping these unique cloud structures.
Horizontal Wind Shear
Horizontal wind shear, which occurs when winds at different altitudes blow in opposite directions or at varying speeds, could also be a contributing factor to Asperitas cloud formation.
Convection Currents
The interaction between layers of air with different temperatures or densities near the Earth’s surface might create convection currents, leading to the development of these peculiar clouds.
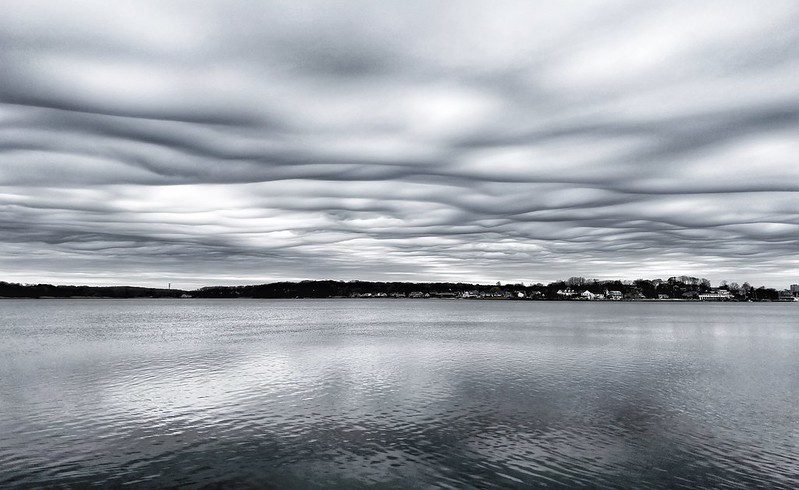

Atmospheric Gravity Waves
Last but not least, atmospheric gravity waves may play a part in this captivating phenomenon. You’re probably wondering: what are “atmospheric gravity waves?”
So, while the exact cause of Asperitas cloud formation remains a mystery, these theories provide some fascinating insights into the complex processes at work in our atmosphere.
Want to learn more about atmospheric gravity waves and their potential influence on Asperitas clouds? No worries. No need to fret – our next section will delve into atmospheric gravity waves and their possible effect on Asperitas clouds.
Gravity Waves and Asperitas Clouds: A Curious Connection
Explore the mysterious realm of gravity waves–not just for astrophysicists, but also affecting our atmosphere and clouds such as the rare Asperitas. They also play a role in shaping our atmosphere and cloud formations, including the rare Asperitas clouds.
Gravity waves occur at the border between two fluids with different densities. They are back-and-forth movements caused by gravity.
How do Gravity Waves Influence Cloud Formations?
When these atmospheric undulations reach cloud level, things get interesting. The resulting turbulence can cause unique patterns within clouds like our beloved Asperitas formations.
Their rough appearance suggests unusual instability at their base layer, which may be due to gravity wave influence propagating downward from above.

What Causes This Instability?
- Orography – terrain effects on weather patterns
- Horizontal wind shear – variations in wind speed or direction over short distances
- Convection currents – vertical air movement driven by temperature differences near Earth’s surface
- Potentially, Asperitas clouds.
Fascinatingly enough, despite all we know about these mesmerizing cloud formations, there is still much to learn about what causes this captivating instability.
Researchers continue to explore the potential role of gravity waves in Asperitas cloud formation. Recent studies have indicated that gravity waves may be a crucial factor in Asperitas cloud formation, though further investigation is necessary to gain insight into their influence.
So next time you spot an Asperitas cloud, remember – there’s more than meets the eye. The mysterious world of gravity waves and their influence on these rare formations continues to captivate both scientists and weather enthusiasts alike.
Capturing Asperitas Clouds on Camera
Are you ready to witness the magic of rare Asperitas clouds?
Well, you’re in luck.
Citizen scientists like Jane Wiggins, who captured a photo resembling Armageddon back in 2006, have paved the way for researchers and enthusiasts alike.
Let’s explore how you can capture these elusive formations too.
Importance of Citizen Science in Capturing Rare Events
The power of citizen science is undeniable.
Thanks to people like Jane, we now have access to images and videos that help us understand these fascinating cloud formations better.
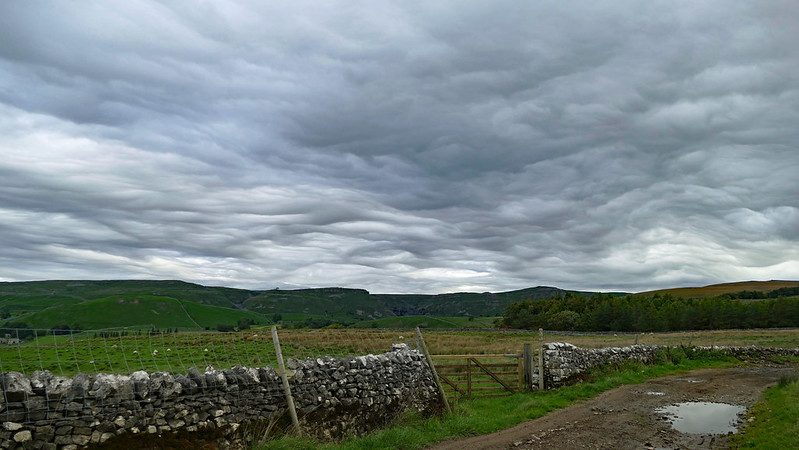

You could be next. So grab your camera or smartphone and keep an eye out for these mesmerizing wonders.
Time-lapse Videos Revealing Atmospheric Complexity
If you happen upon an Asperitas cloud formation, don’t just snap a picture – try capturing it with time-lapse video too.
Time-lapse videos allow us to observe changes over time and reveal intricate details about our atmosphere’s complex fluid dynamics – much like those responsible for choppiness during stormy ocean days.
Tips for Capturing Asperitas Clouds:
- Pick Your Spot: Find a location with an unobstructed view of the sky, preferably away from tall buildings or trees.
- Timing is Key: Asperitas clouds often form during the morning or evening hours when there’s more atmospheric instability.
- Patience Pays Off: These rare formations can be elusive, so keep your eyes peeled and don’t give up.
- Edit & Share: Enhance your photos/videos using editing software and share them on social media to spread awareness about these captivating cloud types.
Become part of the citizen science movement by capturing Asperitas clouds in all their glory – who knows? You might contribute valuable data for researchers worldwide.
Hurry up and join this exciting adventure into the world of rare cloud formations today.
Key Takeaway:
The article discusses the rare Asperitas clouds and how citizen scientists have helped capture them on camera, revealing intricate details about our atmosphere’s complex fluid dynamics. It provides tips for capturing these elusive formations, including picking a spot with an unobstructed view of the sky, being patient, and sharing your photos/videos on social media to spread awareness.
FAQs about Rare Asperitas Clouds
Are Asperitas Clouds Rare?
Yes, Asperitas clouds are considered a rare phenomenon. They were only officially recognized by the World Meteorological Organization in 2017 and have been observed infrequently around the world.
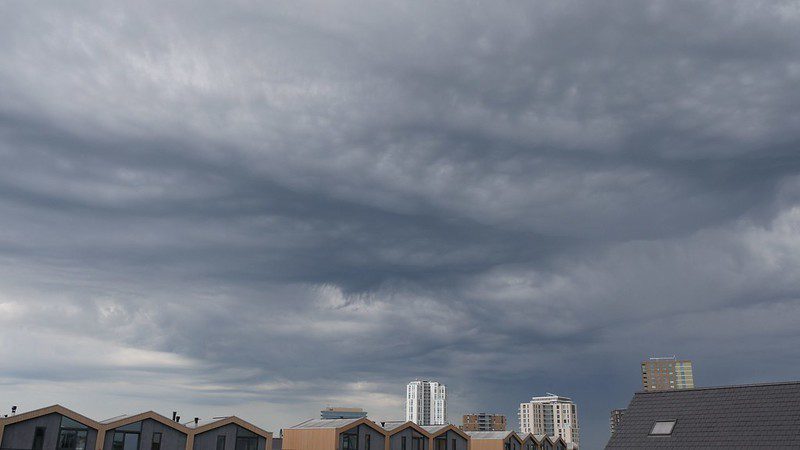
What Does It Mean When You See Asperitas Clouds?
Seeing Asperitas clouds indicates that there is significant atmospheric turbulence and instability at low elevations. These conditions can be influenced by factors such as orography, horizontal wind shear, and convection currents.

What Is the Rarest Type of Cloud?
The rarest type of cloud is arguably the Morning Glory cloud, which occurs primarily in northern Australia during specific times of the year. This unique roll-shaped formation stretches for hundreds of kilometers and requires precise meteorological conditions to form.
Where Are Asperitas Clouds Most Common?
Asperitas clouds, while still quite uncommon globally, have been reported more frequently in regions with complex terrain like mountain ranges or coastal areas where air masses interact dynamically with landforms leading to increased atmospheric turbulence.
Conclusion
Overall, Rare Asperitas Clouds are a fascinating meteorological phenomenon that has only recently been officially recognized by the World Meteorological Organization. These clouds have unique characteristics, such as low-elevation layered structures and highly developed bottom structures with unusual instability at the base layer.
Potential causes for their formation include orography and terrain effects, horizontal wind shear, convection currents, and atmospheric gravity waves. Capturing these rare clouds on camera is important for citizen science efforts to better understand the complexity of our atmosphere through time-lapse videos.
TimsWWW – Tim’s Wierd and Wonderful World Is A Blog About The Natural & Unnatural World