
Natural disasters have caused immense destruction and loss of life throughout history, reminding us of the strength and unpredictability of nature. These occurrences serve as a stark reminder of nature’s immense strength and our fragility in its presence. This blog post will delve into several devastating events that shook various parts of the globe.
We will explore deadly earthquakes such as those in south-central China (2008) and Kashmir, Pakistan (2005), which resulted in thousands of fatalities. We’ll also discuss catastrophic wildfires like Australia’s devastating 2023-2023 bushfires and powerful hurricanes, including Hurricane Maria’s impact on Puerto Rico in 2017.
In addition to these meteorological phenomena, we will touch upon cholera epidemics like Haiti’s outbreak following their earthquake and examine tropical cyclones such as Coringa Southern India Cyclone. Lastly, we’ll study historical disasters in central China, like the great flood of 1931 and earthquakes in Turkey, focusing on the south-central Turkey earthquake predicted for 2023.
This comprehensive account aims to provide an understanding of these biggest natural disasters and shed light on how they have shaped human societies over time.
Deadly Earthquakes in History
Throughout the ages, seismic activity has been responsible for vast destruction and countless deaths. Some of the most devastating earthquakes to ever occur include the 2008 quake in south-central China and a 7.6 magnitude temblor that shook Kashmir, Pakistan, in 2005. These events resulted in numerous deaths and caused considerable damage to buildings and other structures. These disasters resulted in thousands of casualties and massive destruction of infrastructure.
South-central China earthquake (2008)
The south-central China earthquake, also known as the Sichuan or Wenchuan earthquake, occurred on May 12th, 2008, with a magnitude of 7.9. The epicenter was located near Wenchuan County in Sichuan Province, but its effects were felt across a vast area, including Chengdu City and other neighboring provinces like Gansu and Shaanxi.
- Casualties: Approximately 87,000 people lost their lives, while over five million were left homeless due to this catastrophic event.
- Destruction: An estimated $150 billion worth of property damage was reported, along with significant impacts on agriculture and transportation networks throughout affected regions.
- Aftershocks: Over time, there have been more than twenty thousand aftershocks recorded since the main shock took place, some even reaching magnitudes greater than six.
Kashmir, Pakistan earthquake (2005)
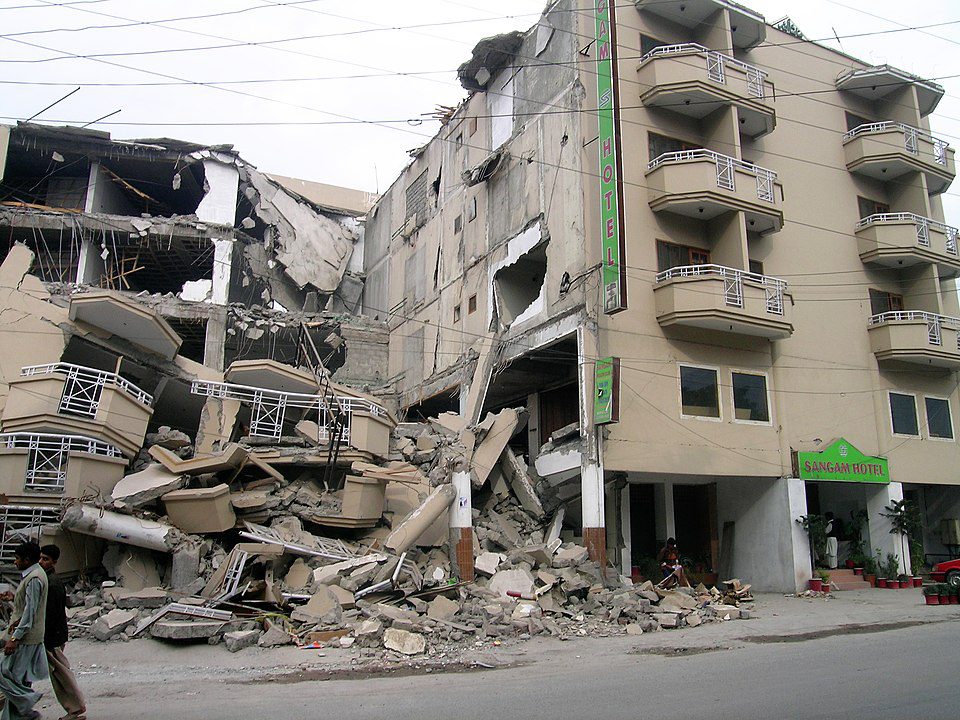

On October 8th, 2005, another devastating natural disaster shook the world when a powerful 7.6-magnitude earthquake struck the Kashmir region in Pakistan. The epicenter was located near Muzaffarabad city, and the tremors were felt as far away as India and Afghanistan.
- Casualties: This tragic event claimed the lives of over 80,000 people while leaving more than four million homeless or displaced from their homes due to extensive damage caused by the quake itself, along with subsequent landslides triggered during the aftershock period that followed the main event.
- Destruction: In addition to the human toll taken on affected communities throughout the region, there was also significant infrastructure loss, including schools, hospitals, roads, bridges, and other vital structures, which made recovery efforts all the more challenging for those involved both locally and internationally alike.
- Aid Efforts: International aid organizations like the Red Cross and the United Nations provided assistance in terms of food, shelter, medical care, and reconstruction support following this devastating natural disaster.
In conclusion, natural disasters like deadly earthquakes can have a significant impact on the world. It is important to be prepared for such events and to take action to mitigate their effects.
Climate change is also a growing concern, and organizations like the Geological Survey, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and Earth Observatory are working to better understand and address its potential impact on natural disasters like extreme rainfall and decimating coastlines. By working together, we can help reduce the death toll and destruction caused by these events.
The 2008 South-central China tremor was a devastating occurrence, leading to the demise of more than 80,000 people. Wildfires have also caused destruction on a global scale; Australia’s 2023 – 2023 wildfires are an example of this destructive power.
Key Takeaway:
The deadliest earthquakes in history have caused widespread devastation and loss of life, such as the 2008 south-central China earthquake and the Kashmir, Pakistan earthquake in 2005. Taking preventive measures to reduce the impact of such disasters is essential, as seen in their aftermaths.
Catastrophic Wildfires
Wildfires are another type of natural disaster that has wreaked havoc on communities throughout history. The 2019–20 Australian wildfires were particularly deadly, causing extensive damage to wildlife habitats as well as human lives lost.

Australia’s Devastating Wildfires (2019–20)
The Australian wildfires during the period of 2019–20 were some of the most destructive in recent memory. These fires burned through millions of acres across multiple states, including New South Wales and Victoria. Homes and properties were destroyed, with many individuals experiencing fatal or serious injuries, in the aftermath of these catastrophic fires.
In addition to the devastating loss of human life, these catastrophic wildfires also had a detrimental effect on Australia’s unique wildlife, with an estimated one billion animals having perished due to habitat destruction caused by the flames. It is estimated that nearly three billion animals perished due to habitat destruction caused by the flames. This includes species such as koalas, kangaroos, wallabies, wombats, and various bird species – many facing potential extinction if recovery efforts do not succeed.
- Ecosystems at risk: The fires severely impacted several key ecosystems within Australia, like rainforests along the Great Dividing Range, which house rare plant and animal populations, and eucalyptus forests, where iconic creatures reside.
- Air quality concerns: Smoke from these massive blazes led to poor air conditions in cities and towns far away, including Sydney and Melbourne, and even reached parts of New Zealand, causing health issues for residents.
- Economic consequences: In addition to environmental damage, wildfires also had significant economic repercussions, with the region’s tourism and agriculture industries affected by destruction and loss of resources.
Although the Australian wildfires of 2023 and 2023 were a tragic reminder of nature’s destructive power, they also served as a call to action for governments, organizations, and individuals around the world. The need for more effective wildfire prevention tactics, environmentally friendly land management methods, and concerted global efforts to fight climate change have become urgently apparent.
Wildfires can be incredibly destructive, leading to the loss of homes, property, wildlife, and ecosystems. Moving on from this tragedy is Hurricane Maria’s impact on Puerto Rico in 2017 which was a destructive hurricane that caused widespread damage throughout the Caribbean islands.
Key Takeaway:
The 2023-2023 Australian bushfires were among the most devastating natural disasters of recent times, with immense damage inflicted on both wildlife habitats and human lives. The fires severely impacted several key ecosystems within Australia, leading to poor air quality concerns and significant economic repercussions for the region’s tourism and agriculture industries. These devastating wildfires served as a call to action for better wildfire prevention strategies, sustainable land management practices, and coordinated efforts to combat climate change.
Devastating Hurricanes
Hurricanes are powerful natural disasters that can cause immense destruction due to their high winds, storm surges, and flooding potential. One such catastrophe occurred when Hurricane Maria struck Puerto Rico on September 20th, 2017. This devastating event became the deadliest U.S.-based natural disaster within a century.
Hurricane Maria’s Impact on Puerto Rico (2017)
The Category 4 storm hit Puerto Rico with winds up to a whopping 250 km/h, leaving many without electricity for months. The intense wind speeds caused widespread power outages across the island, leaving millions without electricity for months. Additionally, heavy rainfall led to severe flooding and landslides throughout the region.
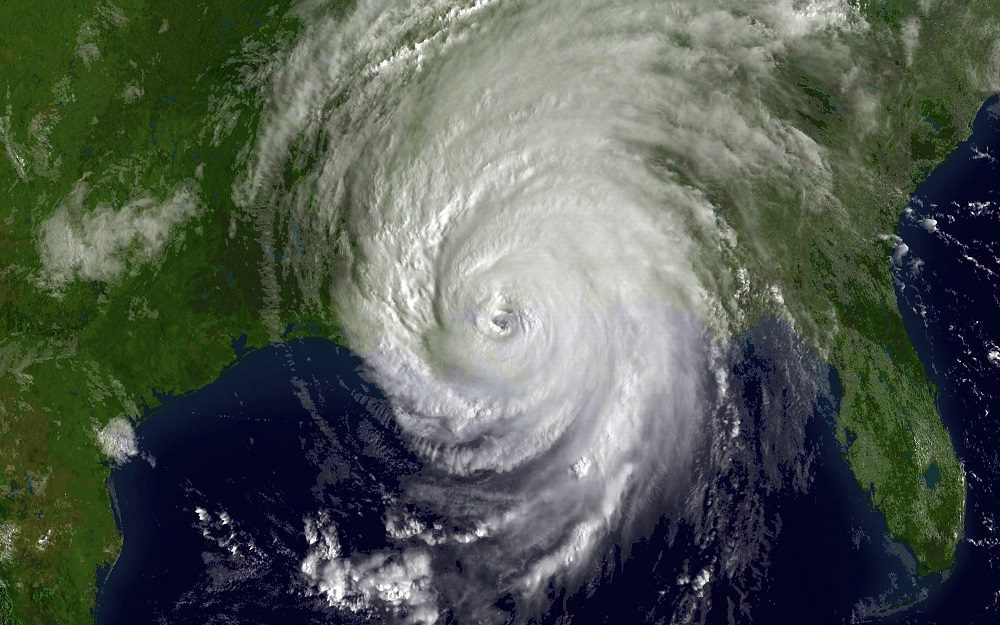

Apart from infrastructure damage, Hurricane Maria had a significant impact on human lives as well. The official death toll was initially reported at around 64; however, subsequent studies have estimated that over 3,000 people lost their lives due to both direct and indirect effects of the storm.
- Direct impacts: These include deaths caused by drowning in floodwaters or being crushed under collapsed buildings during the hurricane itself.
- Indirect impacts: Indirect fatalities resulted from factors like limited access to healthcare services because of damaged hospitals or impassable roads; increased risk of waterborne diseases due to contaminated drinking water sources; mental health issues arising from trauma experienced during and after the disaster, among others.
In response to this catastrophic event, various organizations and individuals stepped up to provide aid and support. For example, the American Red Cross deployed volunteers and resources to help with relief efforts, while celebrities like Lin-Manuel Miranda raised funds through benefit concerts.
Despite these efforts, Puerto Rico still faces ongoing challenges in its recovery process. Many Puerto Ricans are still dealing with the repercussions of Hurricane Maria, including weakened infrastructure and ongoing hardships.
Catastrophic storms have wreaked destruction in multiple regions, with Hurricane Maria’s devastation of Puerto Rico being particularly devastating. Now we turn our attention to cholera epidemics and Haiti’s heartbreaking outbreak following its 2010 earthquake.
Key Takeaway:
Hurricane Maria, a Category 4 storm that made landfall in Puerto Rico in 2017, wreaked havoc with its powerful winds and heavy rains, leading to the loss of over 3,000 lives. The disaster resulted in over 3,000 deaths due to both direct and indirect impacts on human lives. Despite relief efforts from various organizations and individuals, Puerto Rico still faces ongoing challenges in its recovery process.
Cholera Epidemics
Disease outbreaks can also be considered natural disasters when they lead to significant death tolls or societal disruption. One such example is the severe cholera epidemic in Haiti following an earthquake, which further exacerbated its already vulnerable population’s living conditions.
Haiti’s Cholera Outbreak After the Earthquake
In 2010, a devastating 7.0-magnitude earthquake struck Haiti, causing widespread destruction and claiming over 200,000 lives. Following the earthquake, a cholera epidemic spread rapidly due to water sources being contaminated and inadequate sanitation infrastructure.
- The origin: The cholera outbreak was traced back to a United Nations peacekeeping camp where improper waste disposal led to contamination of nearby rivers with Vibrio cholerae bacteria – responsible for causing cholera infections.
- The impact: Since October 2010, more than 820,000 cases of cholera have been reported in Haiti, resulting in over 9,700 deaths. Youngsters below five years of age and those with vulnerable immune systems are most at risk for contracting the illness.
- The response: International organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) stepped up their efforts to provide medical assistance and improve water quality by distributing chlorine tablets for water purification as well as constructing new latrines and sewage treatment facilities.

Beyond immediate relief measures during the epidemic, long-term strategies were implemented to strengthen Haiti’s healthcare system and improve sanitation infrastructure. This included training local health workers in cholera prevention and treatment, as well as investing in the construction of new water supply systems.
Cholera continues to be a major risk in Haiti due to the lack of access to clean water and sanitary facilities. The occurrence serves as a vivid indication of how catastrophes can exacerbate preexisting susceptibilities in societies and result in serious outcomes for public health.
The 2010 Haiti earthquake triggered a particularly disastrous cholera outbreak, resulting in immense suffering and loss of life throughout history. Moving on to tropical cyclones, one of the most destructive storms in recent years was Cyclone Coringa, which struck Southern India in 2018.
Key Takeaway:
The cholera epidemic in Haiti, which followed an earthquake, caused significant fatalities and was a catastrophic event. The outbreak was traced back to improper waste disposal, resulting in contaminated water sources and poor sanitation infrastructure. Intervention by international organizations to help with the Haiti cholera epidemic included medical aid, better water quality measures, instruction of local health personnel in combatting and treating the disease, as well as investing in new systems for supplying clean water, which would bolster healthcare infrastructure and sanitation facilities.
Tropical Cyclones: The Destructive Force of Nature
Tropical cyclones are a powerful force of nature that can cause widespread devastation in their path. As they traverse the seas, tropical cyclones bring with them destructive winds, torrential rains, and towering storm surges. One such tropical cyclone that left a lasting impact on the affected region was the one that hit Coringa in southern India.
Coringa Southern India Cyclone
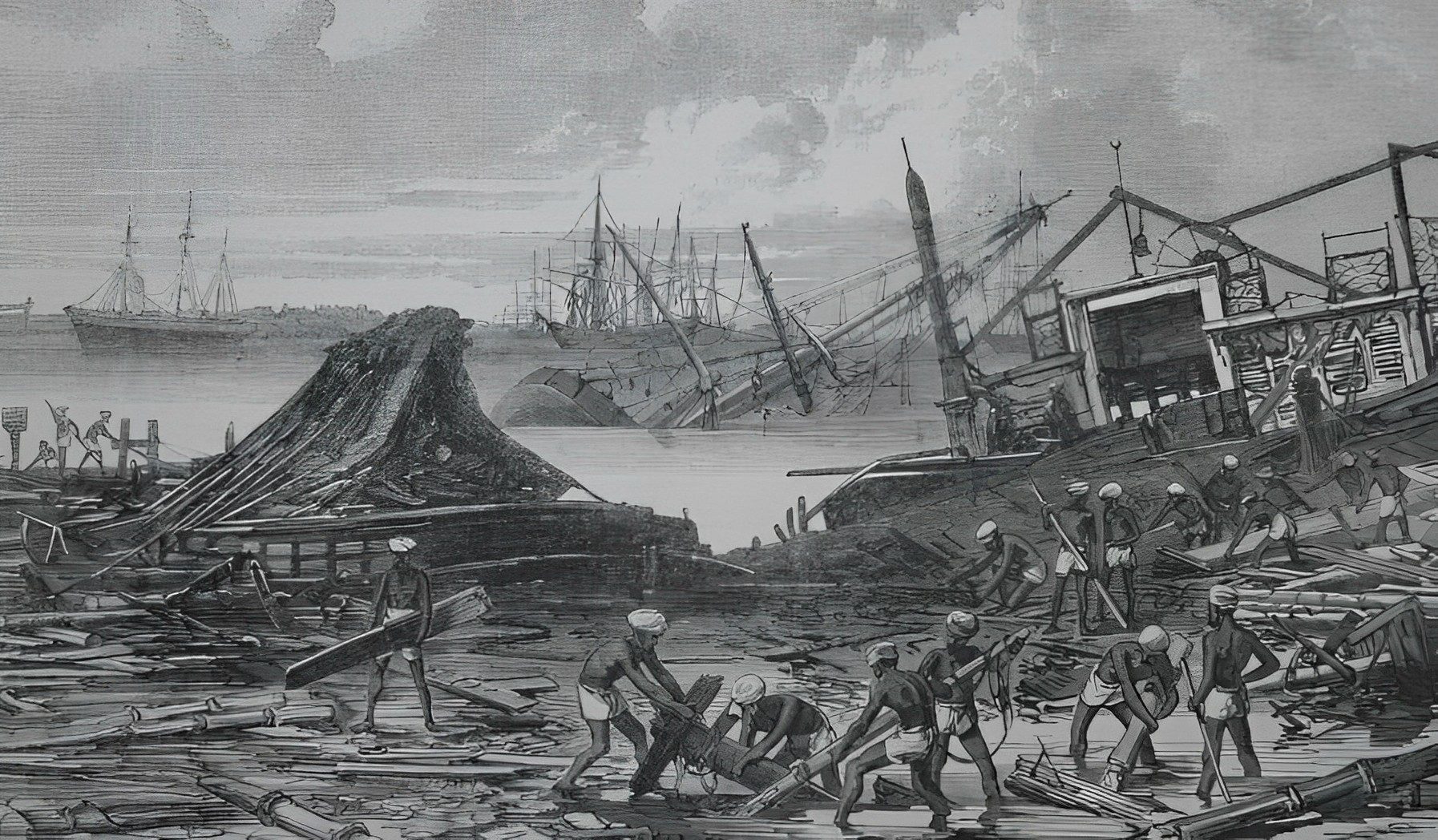

The Coringa cyclone struck southern India in 1839, causing massive destruction to both life and property. The Coringa cyclone, with wind speeds reaching up to 200 km/h (124 mph), wrought havoc on life and property alike, claiming thousands of lives in its wake. Torrential rain exacerbated the already-devastating effects of this cyclone, with flooding leading to additional destruction.
- Wind Speeds: Tropical cyclones like the one that hit Coringa can have incredibly strong wind speeds capable of leveling entire towns or cities within hours.
- Rainfall: Heavy rainfall is another significant factor associated with these storms; it often leads to devastating floods and landslides, which add even more destruction than caused by high winds alone.
- Storm Surges: Coastal areas are particularly vulnerable during tropical cyclones due to rising sea levels brought about by storm surges – waves created from intense low-pressure systems pushing water towards land masses at an alarming rate; these surges can lead not only to coastal erosion but also to widespread inundation inland too.
In order for communities to better prepare for and mitigate the impacts of tropical cyclones, it is essential that they have access to accurate weather forecasts and early warning systems. By staying informed about potential threats, residents can take necessary precautions such as evacuating high-risk areas or reinforcing their homes against strong winds.
Understanding the destructive force of tropical cyclones is crucial in order to develop effective strategies for reducing their impact on vulnerable populations. As climate change continues to alter weather patterns around the world, it becomes even more important that we work together globally towards finding solutions that minimize damage caused by these powerful storms while also ensuring affected communities are able to recover quickly from any devastation left behind in their wake.
Tropical cyclones are a powerful force of nature that can cause immense destruction yet also bring about much-needed rain and relief. Disasters in Central China have been recorded for centuries, with the Great Flood of 1931 being one of the most devastating to ever occur.
Key Takeaway:
Tropical cyclones are a destructive phenomenon, capable of wreaking havoc through powerful winds, heavy rainfall and storm surges. The Coringa cyclone in southern India in 1839 claimed thousands of lives and destroyed countless homes and infrastructure along its path due to wind speeds reaching up to 200 km/h (124 mph) and severe flooding caused by torrential rains. Accurate weather predictions and advanced alerts are essential for communities to ready themselves for these cyclones, while the international community must strive to reduce their effect on those in danger as climate change alters global meteorological conditions.
The Great Flood of 1931 in Central China
Between June and August 1931, a series of devastating floods wreaked havoc across Central China, resulting in one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history. The catastrophe was caused by excessive rainfall that led to swollen rivers, which ultimately overflowed their banks and inundated vast areas.

The primary rivers affected during this disaster were the Yangtze, Huai, and Yellow Rivers. These three major waterways experienced unprecedented levels of flooding due to a combination of factors, including snowmelt from the mountains, unusually heavy rainfalls during the spring season, and poorly maintained levees that failed under pressure.
- Yangtze River: The longest river in Asia experienced massive flooding along its course through central China. This resulted in widespread destruction as cities like Wuhan were submerged under several meters of water.
- Huai River: A tributary of the Yangtze River also faced significant flooding which further exacerbated the overall devastation throughout Central China.
- Yellow River: Known as “China’s Sorrow,” this river is infamous for its frequent floods. In 1931, it contributed greatly to what would become one of humanity’s most tragic events when it, too, burst its banks, causing untold damage across multiple provinces.
An estimated 140 million people were directly impacted by these catastrophic floods, with millions displaced from their homes or left without access to basic necessities such as food or clean drinking water. According to some estimates, between one million and four million lives were lost due to drowning or subsequent disease outbreaks like cholera among survivors living in unsanitary conditions.
Despite the immense scale of this disaster, it remains relatively unknown outside of China. The effects of the tragedy on Chinese society were immense and long-lasting. In response to the 1931 Great Flood, China’s government implemented the Great Leap Forward initiative to strengthen flood control systems and modernize infrastructure along major rivers like the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers.
The Great Flood of 1931 serves as an important reminder that natural disasters can strike with little warning and have far-reaching consequences for affected populations. It also highlights the importance of investing in robust infrastructure projects designed to mitigate potential risks associated with extreme weather events or other environmental hazards.
The great flood of 1931 in Central China was a devastating event that caused much destruction and loss of life. Earthquakes have also been a major natural disaster in Turkey, the most recent being the South-central Turkey earthquake of 2023.
Key Takeaway:
Excessive precipitation caused rivers to swell, resulting in the Great Flood of 1931 in Central China – one of history’s most devastating natural disasters. An estimated 140 million people were directly impacted, with between one and four million lives lost due to drowning or subsequent disease outbreaks among survivors living in unsanitary conditions. The tragedy serves to emphasize the importance of investing in resilient infrastructure projects, which could help reduce potential risks from extreme weather conditions or other environmental hazards.
Earthquakes in Turkey
Turkey is no stranger to earthquakes, with its location on several fault lines, making it prone to seismic activity. One such event was a magnitude 7.8 earthquake that struck south-central Turkey on February 6th, which resulted in significant destruction and casualties.
South-central Turkey Earthquake (2023)
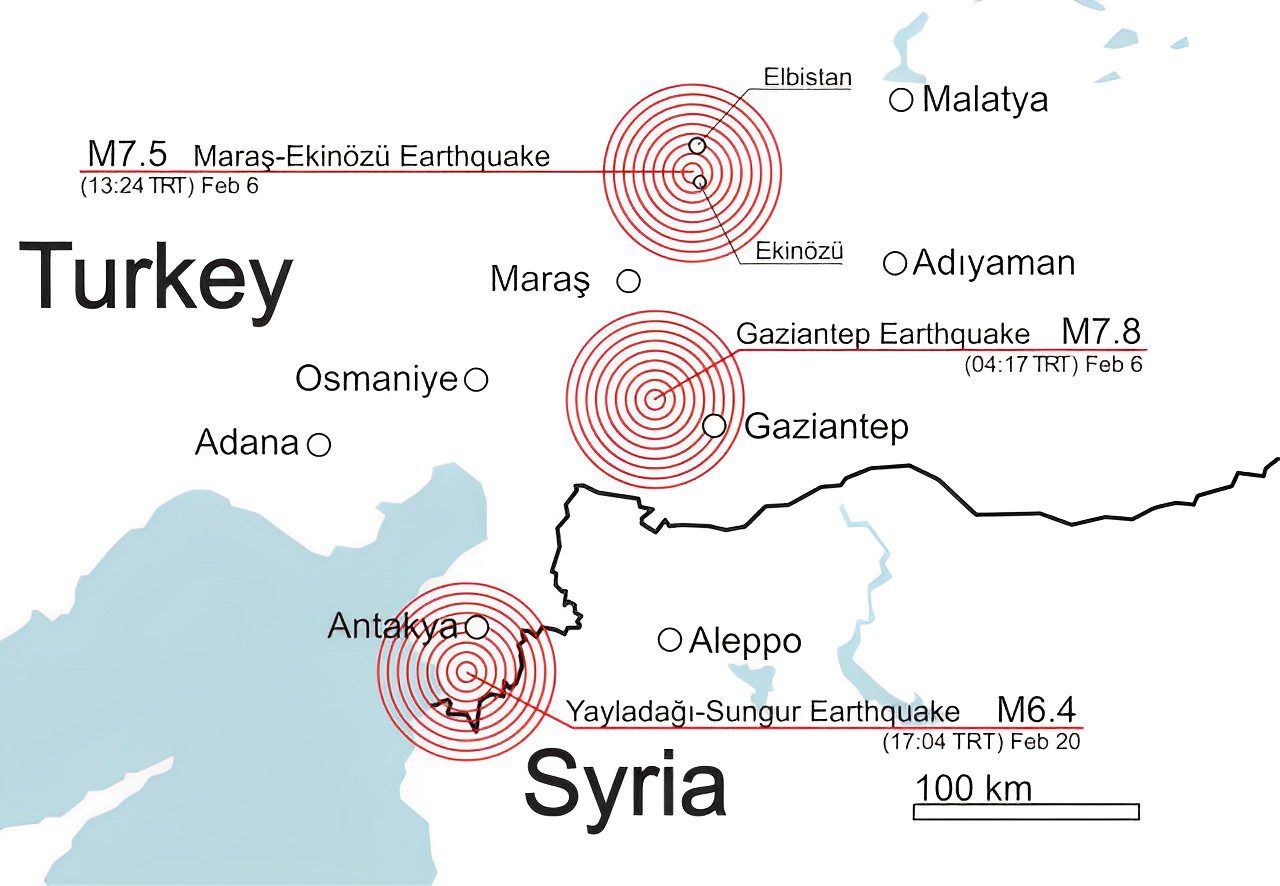
On February 6, 2023, a devastating magnitude 7.8 earthquake wreaked havoc on south-central Turkey with tragic consequences. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) reported that the quake’s epicenter was located near the city of Afyonkarahisar and affected several surrounding provinces.
The death toll from this catastrophic event reached into the thousands as buildings collapsed and infrastructure crumbled under the intense shaking. Rescue efforts were hampered by ongoing aftershocks, extreme rainfall, and limited resources due to previous natural disasters in other parts of the country.
- Aftershocks: Following the initial quake, numerous aftershocks continued to rock the region for weeks afterward – further damaging already weakened structures and complicating rescue operations.
- Rainfall: Heavy rains following closely behind caused additional problems, such as landslides and flooding – exacerbating an already dire situation for those affected by this disaster.
- Limited Resources: With emergency response teams stretched thin across multiple regions dealing with various natural disasters like wildfires and floods, the ability to respond quickly and effectively to this earthquake was hindered.
As a result of these compounding factors, many communities were left decimated – with survivors struggling to rebuild their lives amidst ongoing aftershocks and extreme weather conditions. The international community rallied together in support of Turkey during this difficult time, providing much-needed aid and assistance through organizations like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and various non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
The south-central Turkey earthquake serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of natural disasters on our planet. It is essential for countries everywhere to commit to getting ready for disasters, including the installation of alarm systems, upgrades in infrastructure, and training programs for emergency response, if we are to limit fatalities from severe weather events that have been made worse by climate change.
Key Takeaway:
In February 2023, a magnitude 7.8 earthquake hit south-central Turkey, causing significant destruction and loss of life. The catastrophic event was worsened by the succession of tremors, torrential rain, and a dearth of resources as a result of prior natural disasters in other areas. This serves as a warning to governments worldwide that they should invest in measures of readiness for disasters so as to reduce the casualties resulting from severe weather conditions worsened by climate change.
FAQs in Relation to Biggest Natural Disasters
What is the biggest natural disaster ever?
The 1931 China floods are considered the biggest natural disaster in recorded history, causing an estimated death toll of 1-4 million people. The event resulted from a combination of snowmelt and heavy rainfall that led to widespread flooding along the Yangtze River basin.
What is the number 1 deadliest natural disaster?
The deadliest single-event natural disaster was the 1556 Shaanxi earthquake in China, which claimed approximately 830,000 lives. This catastrophic quake devastated entire cities and caused massive landslides throughout central China’s Hua County region.
What are some of the biggest natural disasters?
- 1931 China floods
- 1556 Shaanxi earthquake
- 1770 Bengal Famine
- 1970 Bhola cyclone
- 1976 Tangshan earthquake

What are the 7 natural disasters?
The seven main types of natural disasters include:
- Earthquakes
- Volcanic eruptions
- Tsunamis
- Floods
- Droughts
- Hurricanes and typhoons
- Wildfires
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), natural disasters are becoming more frequent and severe due to climate change. Extreme rainfall and deadly earthquakes are just some of the consequences of this phenomenon. The Geological Survey and Earth Observatory are constantly monitoring these events to better understand and predict their impact.
One of the most devastating natural disasters in recent history was the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, which killed over 230,000 people and decimated coastlines in several countries. This tragedy served as a wake-up call for the world to take action against climate change and its consequences.
It’s important to note that the death toll from natural disasters is not just a number. Each life lost represents a family, a community, and a world forever changed. Let’s work together to mitigate the effects of climate change and prevent further loss of life.

Conclusion
From devastating earthquakes to raging wildfires, the world has endured some of its most catastrophic natural disasters. These events have caused widespread destruction and loss of life, leaving behind a trail of devastation that takes years to recover from.
While we cannot prevent natural disasters from occurring, we can take steps to prepare for them and minimize their impact on our communities. By staying aware of potential risks and joining forces as a worldwide society, we can lessen the effects of these disasters and safeguard those most at risk.
The death toll from natural disasters has been on the rise in recent years, with climate change playing a significant role in the frequency and severity of these events. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s National Centers for Environmental Information, the total number of deaths from natural disasters in 2023 alone was over 8,000.
The United States Geological Survey and Earth Observatory have reported that the Indian Ocean and South Pacific are particularly vulnerable to natural disasters, with tsunamis and cyclones decimating coastlines and causing widespread damage.
It is important that we continue to invest in research and technology to better understand and predict natural disasters, as well as develop strategies to mitigate their impact. By working together, we can help protect our communities and ensure a safer future for all.

































































