
The Facts
- Most Common Name: Blue-Footed Booby
- Scientific Name: Sula nebouxii
- Type of Animal: Birds
- Diet: Carnivore
- Group of Birds: Flock
- Natural Life Span: 17 years
- Dimensions: 32 to 34 inches; wingspan: nearly 5 feet
- Weight: 3.25 pounds
Introduction to the Unique Blue-Footed Booby Bird
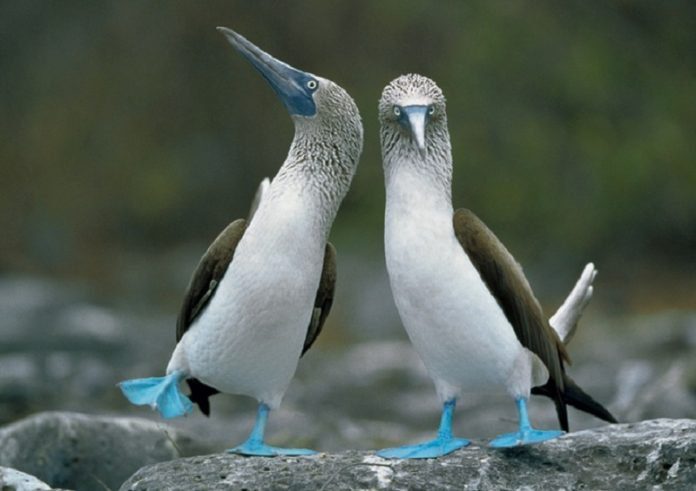
The blue-footed booby (Sula nebouxii) is a unique marine bird indigenous to the eastern Pacific Ocean’s subtropical and tropical areas. It is one of 6 species of the genus Sula – identified as boobies. It is easily recognisable by its unique bright blue feet, which is a sexually selected characteristic.
Males present their feet in an elaborate mating ceremony by lifting them up and down while swaggering before the female. The female is somewhat bigger than the male and can measure up to 90 cm (35 in), including a wingspan up to 1.5 m (5 ft).
The Blue-Footed Booby’s Habitat
The natural breeding environments of the blue-footed booby are the tropical and subtropical isles of the Pacific Ocean. It can be located from the Gulf of California south on Central and South America’s western coasts to Peru.
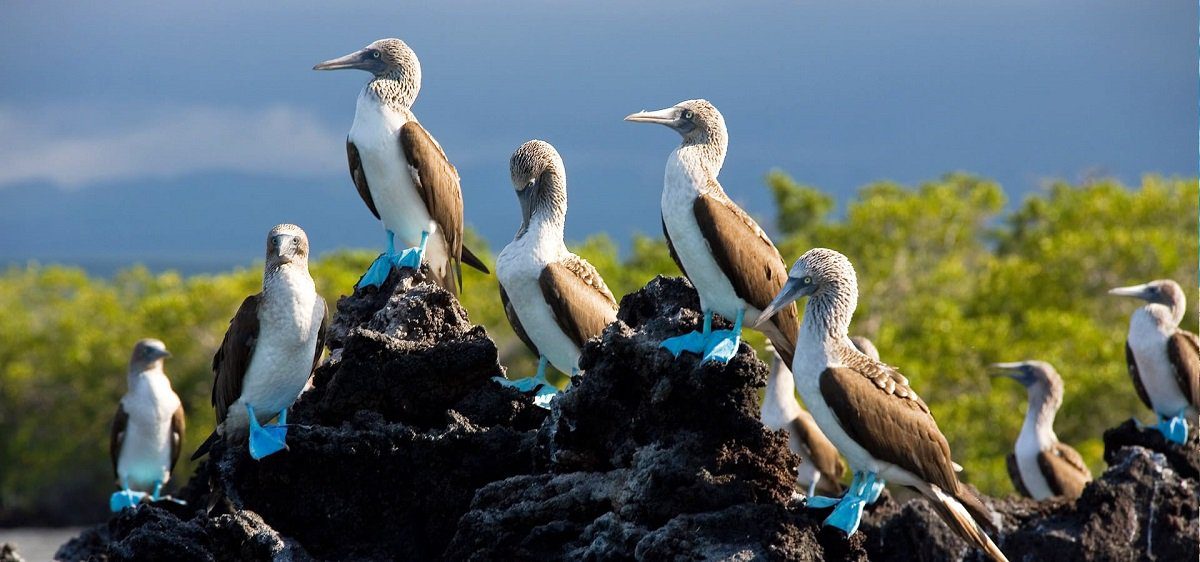
About half of all breeding couples nest on the Galápagos Islands. Its diet primarily consists of fish, which it gets by diving and sometimes swimming underwater searching for its prey. It sometimes hunts alone but hunts typically in groups.

The blue-footed booby lays typically one to three eggs at a point. The species exercises asynchronous hatching, in contrast to many other species. Incubation occurs when the last egg is laid, and all chicks hatch together.
This results in a growing inequality and size difference between siblings, leading to facultative siblicide in food scarcity incidents. This makes the blue-footed booby an essential model for investigating parent-offspring conflict and sibling rivalry.
History
The blue-footed booby was defined by the French naturalist Alphonse Milne-Edwards in 1882 following the current binomial name Sula nebouxii.
The specific epithet was picked to honour the surgeon, naturalist, and adventurer Adolphe-Simon Neboux (1806-1844). There are two recognised subspecies:
- S. n. nebouxii Milne-Edwards, 1882 – Pacific shoreline of Southern and Middle America
- S. n. excisa Todd, 1948 – Galápagos Islands
Its nearest relative is the Peruvian booby. The two varieties likely split from each other recently due to their shared environmental and biological characteristics. A 2011 investigation of multiple genes estimated the two species deviated between 1.1 and 0.8 million years ago.
What does The Blue Footed Bobo Mean?
The name booby arises from the Spanish word bobo (“stupid”, “foolish”, or “clown”) because the blue-footed booby is, like different seabirds, clumsy on land.
They are also considered as foolish for their apparent fearlessness of humans.
What Does The Blue-Footed Booby Look Like?
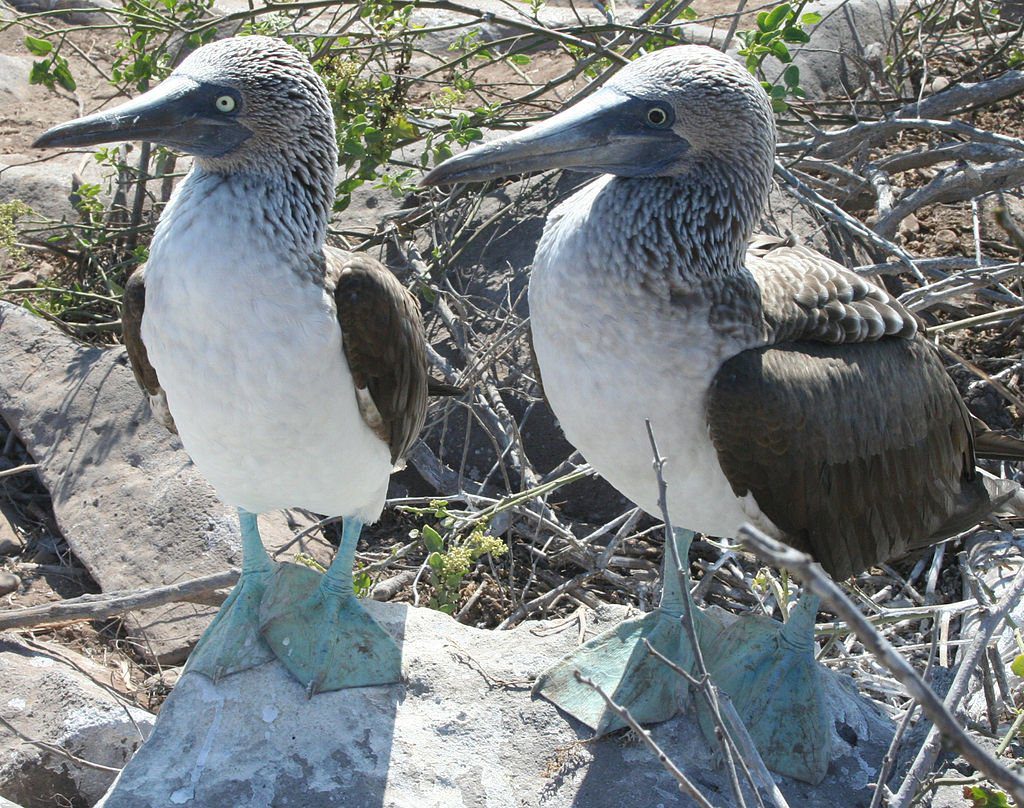

The male has a tinier pupil and slightly lighter feet and is tinier in size than the female.
The blue-footed booby is on usually 81 cm (32 in) tall and weighs 1.5 kg (3.3 lb), with the female being marginally bigger than the male. Its wings are long and pointed, and brown in colour.
The neck and head of the blue-footed booby consist of light browns with white stripes, while the belly and base exhibit pure white plumage. Its eyes are located on either side of its bill and turned towards the front, enabling superior binocular vision.
Its eyes are a distinctive yellow, and the male producing more yellow in its irises than the female. Blue-footed booby juvenile chicks have black beaks and feet and are clad in the soft white layer.

The subspecies S. n. excisa that reproduces on the Galápagos Islands is larger than this variety subspecies and has lighter plumage particularly around the neck and head.
The Peruvian booby is comparable in appearance but has grey feet, whiter head and neck, and white spots on its wing coverts. The areas of the two species overlap in the oceans of northern Peru and southern Ecuador.
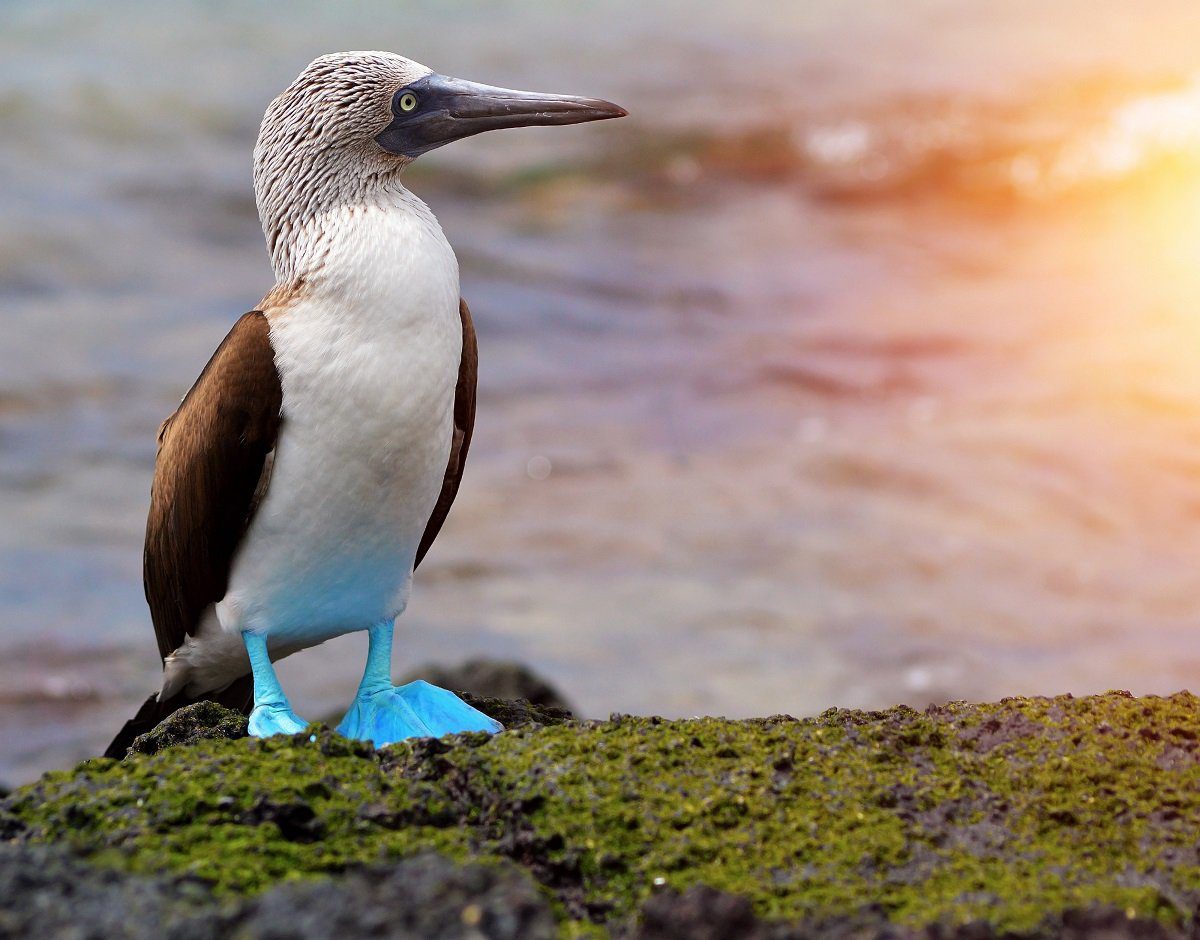
Considering the blue-footed booby preys on fish by plunging headlong into the water, its nostrils are forever closed, and it has to breathe through the edges of its mouth.
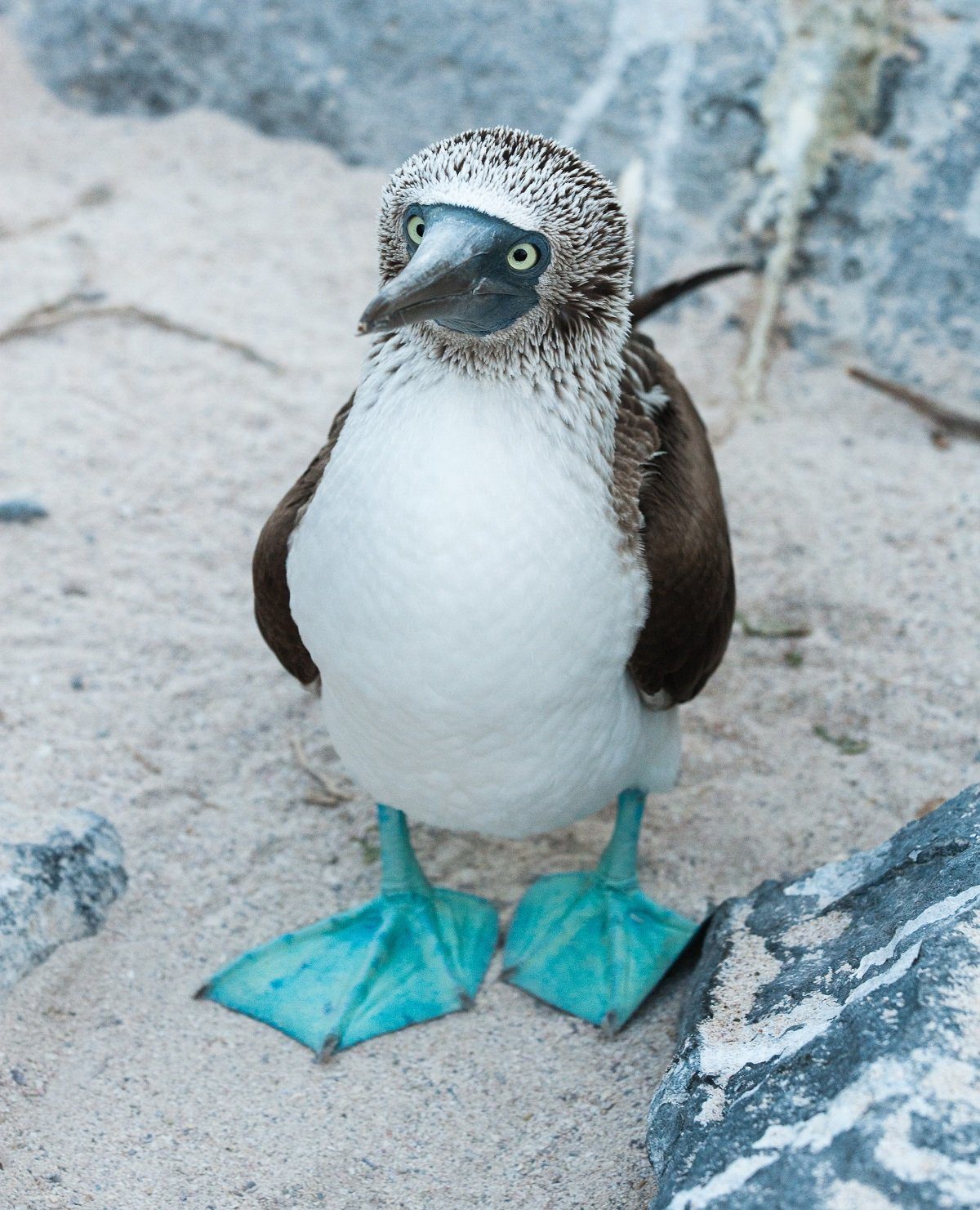
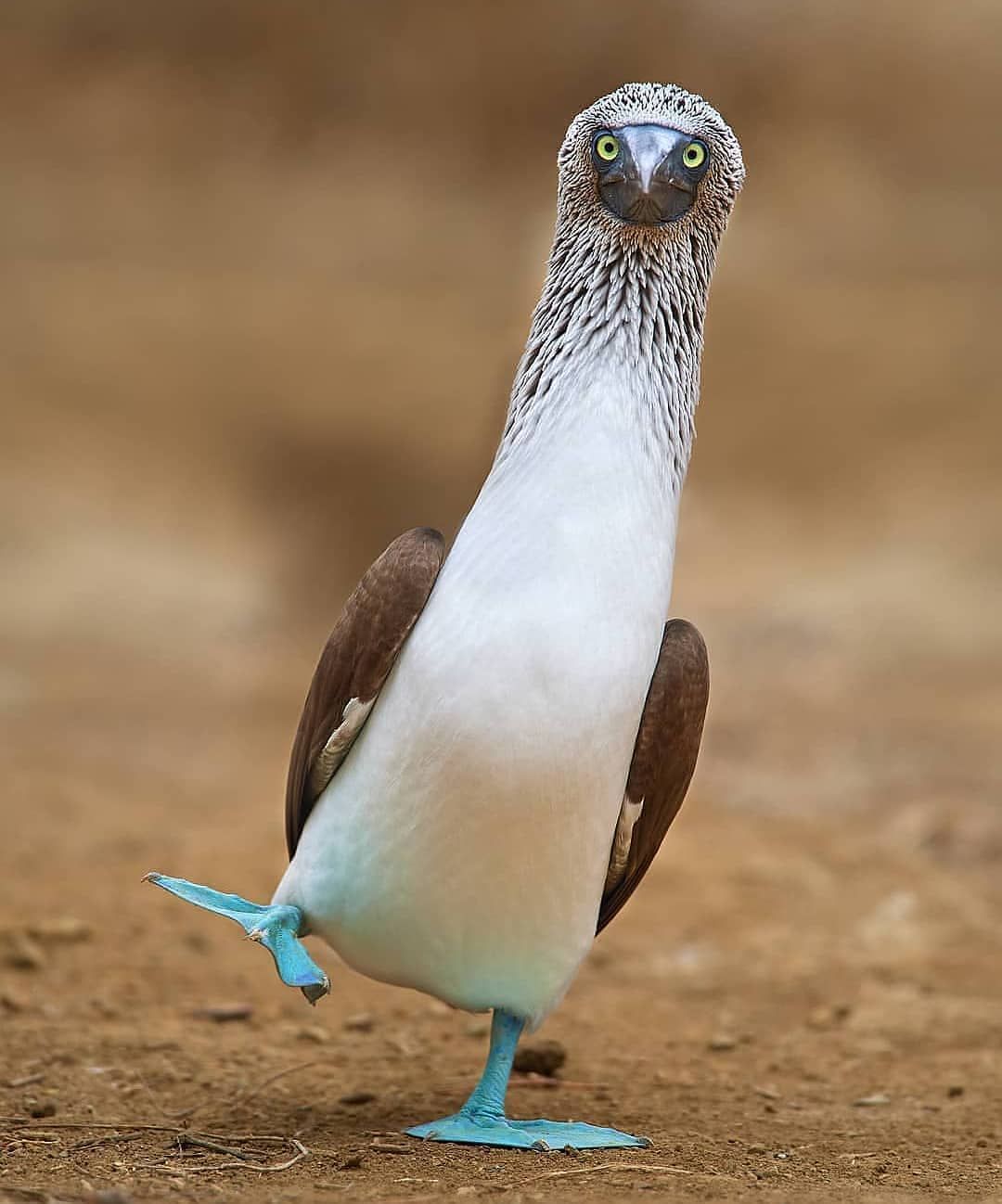
Its most noticeable characteristic is its blue-coloured feet, ranging in colour from pale turquoise to a deep aquamarine. Males and more juvenile birds have lighter feet than females.
Its blue feet play a crucial role in courtship rituals and breeding. The male visually presents his feet to attract mates through the breeding season.
Distribution and Habitat
The blue-footed booby is spread among the eastern Pacific Ocean’s continental shores from California to the Galápagos Islands south toward Peru. It is stringently a marine bird. Its only requirement for the land is to breed and rear young, which it does on the eastern Pacific’s rocky coasts.
A booby may use and protect two or three nesting sites, consisting of exposed black lava in small crevices in the ground until they acquire a favourite one a few weeks before the eggs are deposited.
These nests are built as parts of large colonies. While nesting and brooding, the female turns to face the sun during the day, so the nest is circled by excrement.
Foot Pigmentation
The blue-footed booby’s webbed feet blue colour arises from carotenoid pigments from its raw fish diet. Carotenoids act as antioxidants and energisers for the blue-footed booby’s immune capacity, suggesting that carotenoid pigmentation is a pointer of an individual’s immunological state.
Blue feet also show the current health condition of a booby. Boobies that were experimentally deprived of food for 48 hours encountered a reduction in foot brightness due to a decrease in the number of lipids and lipoproteins utilised to absorb and transport carotenoids.
Thus, the feet are fast and honest indicators of a booby’s general level of nourishment. As blue feet are signs that reliably indicate the immunological and health status of a booby, colouration is favoured through sexual selection.
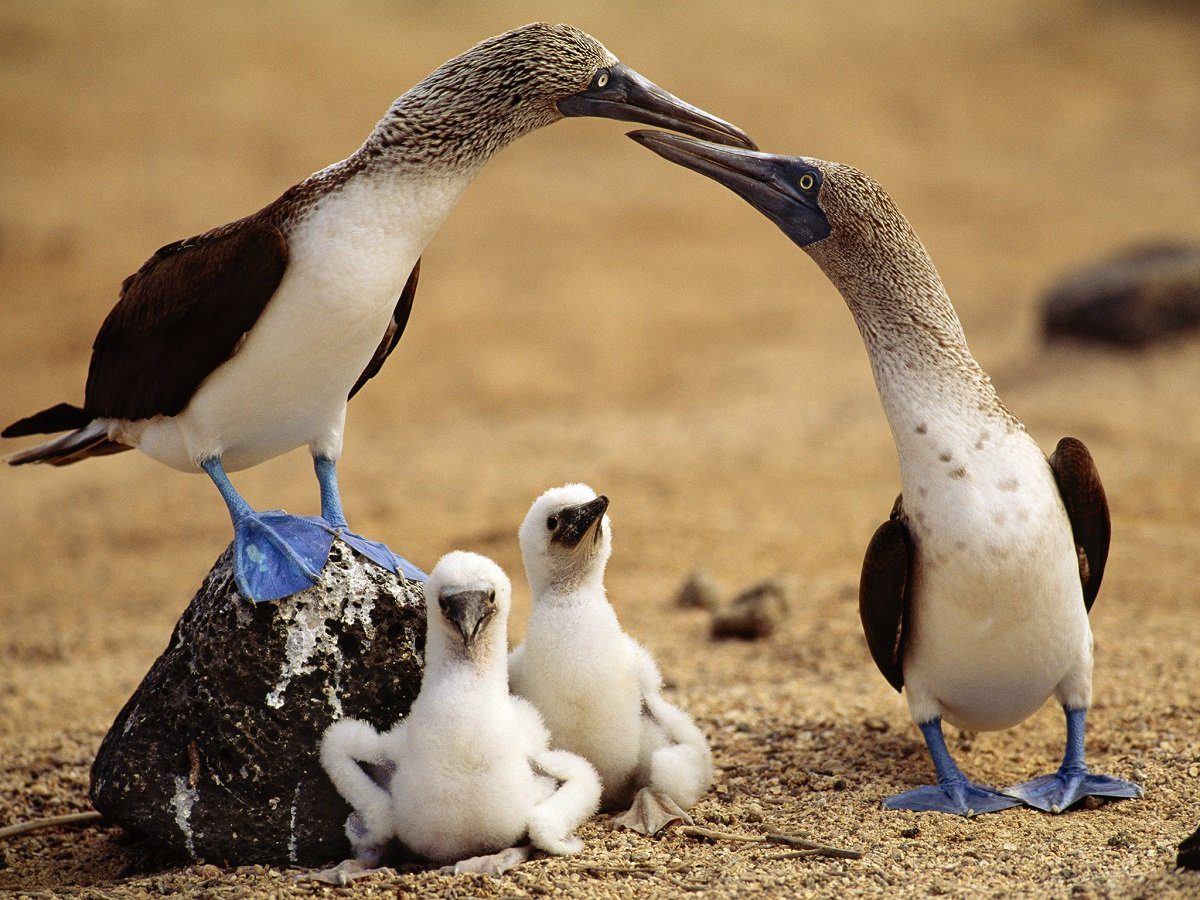

Reproduction
Female Selection
The brightness of the feet diminishes with age, so females favour to mate with more youthful males with brighter feet, which have better fertility and better ability to give paternal care than older males.
In a cross-fostering experiment, foot colour reflects paternal participation in raising chicks; chicks reared by foster fathers with brighter feet developed faster than chicks reared by foster males with duller feet.
Females continuously assess their partners’ health based on foot colour. In one experiment, males whose companions had laid the first egg in the nest had their feet dulled by make-up.
The female companions laid smaller second eggs a few days following. As duller feet typically indicate a decrease in health and perhaps genetic quality, it is adaptive for these females to reduce their second egg investment.
The smaller second eggs included less yolk concentration, affecting embryo development, hatching success, and consequent chick growth and survival.

Also, they contained less yolk androgens. As androgen plays a vital role in chick survival, the experiment implied female blue-footed boobies use the attractiveness and observed genetic quality of their mates to decide how much resources they should designate to their eggs.
This supports the differential allocation theory, which foretells that parents invest longer in their offspring’s care when matched with attractive mates.
Male Selection
According to their partner’s status, males also assess their partner’s reproductive value and modify their own investment in the offspring according to their partner’s status.
Females that lay bigger and brighter eggs are in better status and have more excellent reproductive value. Consequently, males tend to exhibit higher attentiveness and parental care to larger eggs, since they were created by a female with an apparent good genetic condition.
Smaller, duller eggs earned less paternal care. Female foot colour is also seen as an indication of the perceived female condition. In one experiment, the colour of eggs was reduced by researchers, males were prepared to exercise comparable care for both large eggs and small eggs if their mate had brightly coloured feet.
In contrast, males joined with dull-footed females only incubated larger eggs. Researchers also discovered that males did not improve their care when females showed both bright feet and high-quality children.

Hunting, Feeding and Diet
The blue-footed booby is a specialised fish eater, grazing small schooling fish including sardines, mackerel, anchovies and flying fish. It will likewise take squid and offal. The blue-footed booby hunts and forages by diving into the sea after prey, sometimes from a high height, and can swim underwater to pursue its target.
It can hunt individually, in pairs, or in more extensive flocks. Boobies travel in crowds of about 12 to areas of ocean with large schools of small fish. When the lead or point bird sees a fish shoal in the sea, it indicates to the remainder of the group, and they all dive in cooperation, facing their bodies down like arrows.
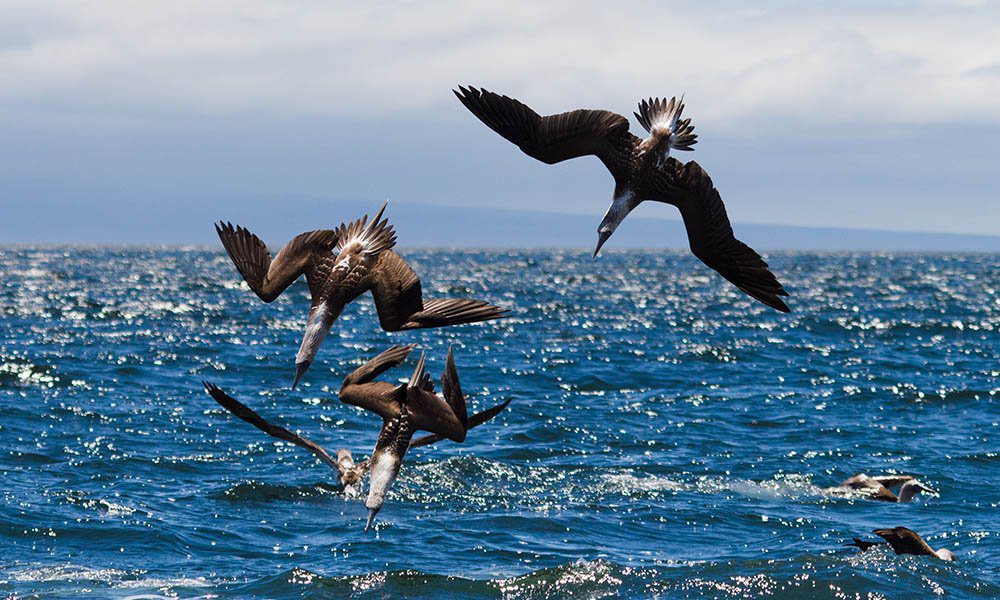

Plunge diving can be made from heights of 10–30.5 m (33–100 ft) and also up to 100 m (330 ft). These beautiful birds hit the water approximately 97 km/h (60 mph) and can drop 25 m (82 ft) underneath the water surface. Their skulls include special air sacs that shield the brain from enormous pressure.
Prey is regularly eaten while the birds are still underwater. Individuals prefer to eat independently rather than with their hunting group, generally in the early mornings or late afternoons. Males and females fish in different ways, which may contribute to why blue-foots, unlike different boobies, grow more than one young.
The male is smaller and has a proportionally longer tail, enabling the male to fish in shallow sections and deep waters. The female is larger and can carry more fish. Both the male and female feed the chicks by regurgitation.
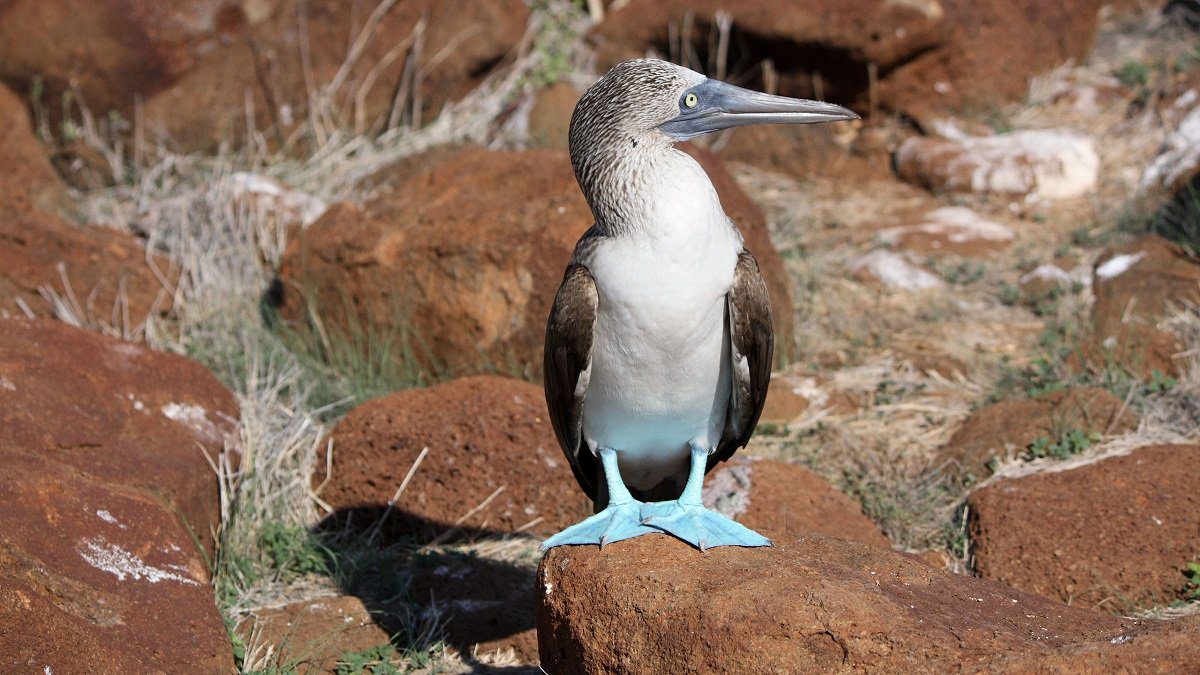

Breeding
The blue-footed booby is a monogamous bird, although it can have more than one mate at the same time. It is an opportunistic breeder, with the breeding period transpiring every 8 to 9 months.
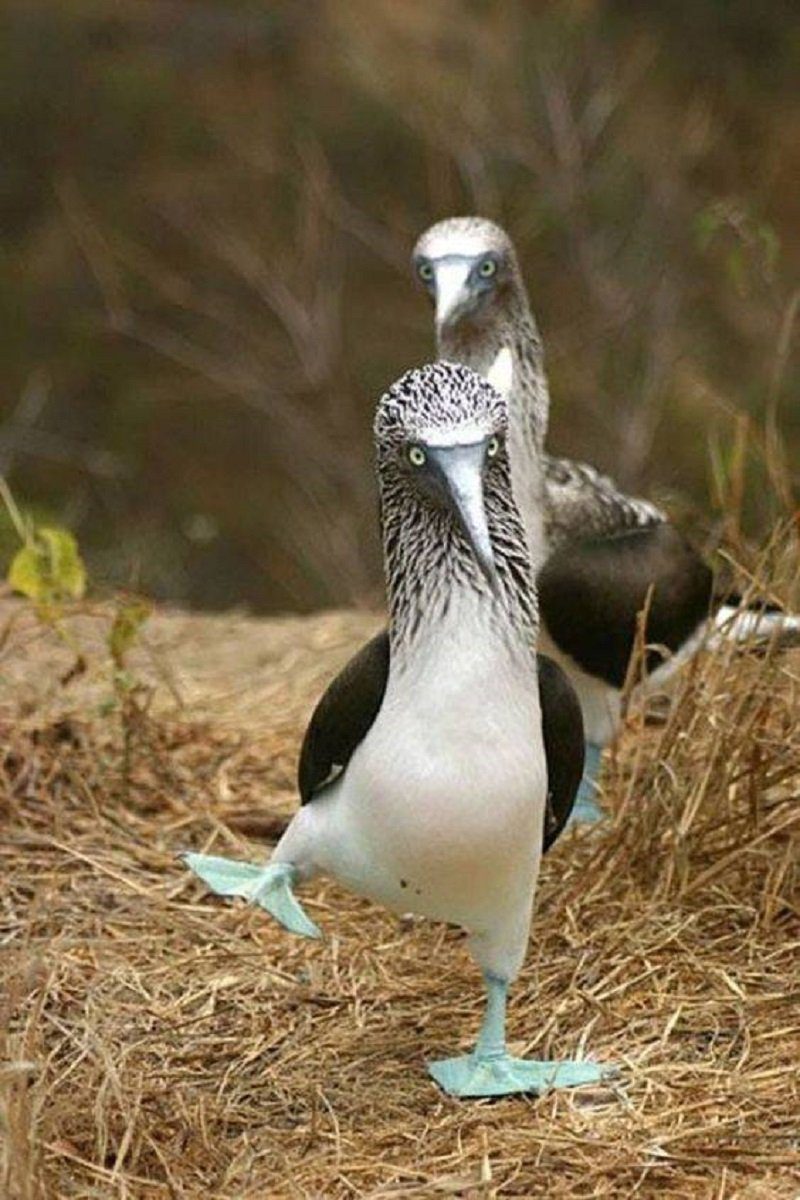
The blue-footed booby’s courtship consists of the male displaying his blue feet and dancing to dazzle the female. The male begins by showing his feet, swaggering in front of the female. Then, he presents nest materials and ends the mating ritual with a final display of his feet.
The dancing also includes “sky-pointing”, which consists of the male pointing his head and bill up to the sky while maintaining the wings and tail in a raised fashion.
Rearing Young
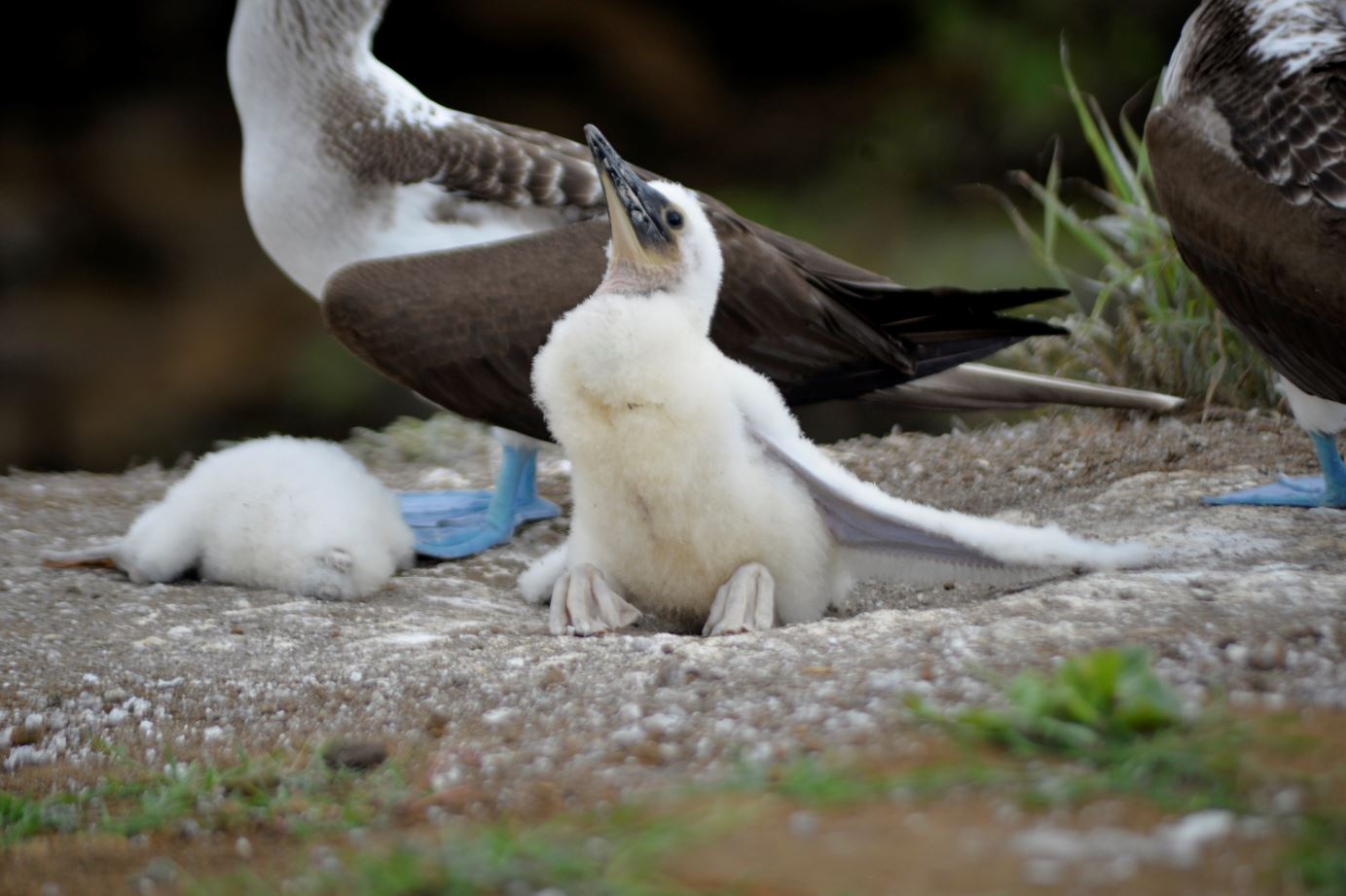

The blue-footed booby is one of only two varieties of booby that parents more than one chick in a breeding cycle.
The female blue-footed booby produces two or three eggs, of four to five days apart. Both male and female take shifts incubating the eggs, while the non-sitting bird keeps guard. Since the blue-footed booby does not own a brooding patch, it uses its feet to keep the eggs warm.
The incubation phase is 41–45 days. Ordinarily, one or two chicks are hatched from the two or three eggs laid initially—the male and female share parental responsibilities. The male provides food for the newborn in the first part of their lives because of his specialised diving techniques.
The female takes over when the demand is higher. Chicks feed off the regurgitated fish in the adult birds mouth. If the parent blue-footed booby does not have sufficient food for all of the chicks, it will only feed the largest chick, guaranteeing that at least one will survive.
Communication
The Blue-Footed Booby Bird Call
Blue-footed boobies make raucous, loud or polysyllabic grunts or shouts and thin whistling sounds. The species’ males have been identified to thrust up their heads and whistle at a fleeting, flying female. Their ritual performances are also a form of communication.
Mates can identify each other by their calls. Although calls differed among sexes, unique characteristic signatures were present. Both males and females can distinguish the calls of their mates from others.

Population Decline
The attention of a decline in the booby population of the Galápagos Islands urged a research project in its cause. The plan, created in April 2014, reinforced the population decline.
The blue-footed booby population seems to be having trouble breeding, thus is gradually declining. The decline is feared to be long-term, but yearly data collection is needed to determine that this is not a natural fluctuation.
Food difficulties may be the foundation of a recognised failure of the birds to even try to breed. This is linked to a decline in sardines (Sardinops sagax), an essential part of the boobies’ diet. Earlier work on Española Island had prosperous breeding in blue-footed boobies that have access to sardines.

In this event, their diet consists primarily wholly of sardines. Still, sardines have mainly been removed from the Española area since 1997, as shown from Nazca boobies there, which also favour sardines, but can reproduce using other prey.
In 2012–13, approximately only half of prey items in the boobies’ diet were sardines. No indication was seen of other possible explanations for the decline, such as humans’ effects, introduced predators, or diseases and pests.


































































Wonderful!!! I love ❤ these precious birds…thank you!
Yes, they are unique, but all wildlife and nature is unique 😍