Introduction
Bumblebee bats (Craseonycteris thonglongyai) or AKA Kitti’s hog-nosed bats are found in limestone caves near waterways in the forests of Thailand and Myanmar. These miniature mammals only ever stray approximately 0.62 miles (1 kilometre) from their nest or home cave.
The principal menace to these bats is interference by humans. Humans frequently visit those bats caves for tourism. Bats are gathered and dried for sale as mementoes, or people disrupt them while collecting their guano for fertiliser, which is utilised to enhance the nutritional value of vegetable yields.
Range and Habitat
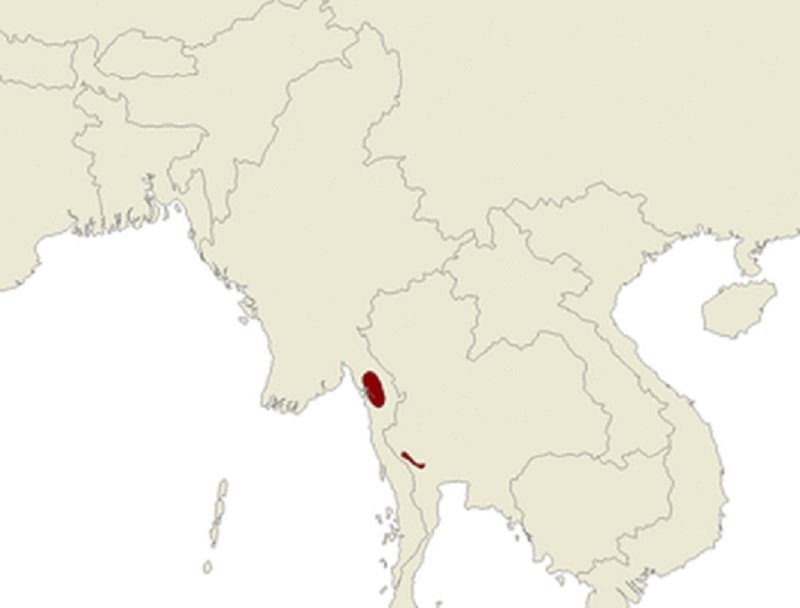
Kitti’s hog-nosed bat occupies limestone caves on rivers in dry evergreen or deciduous forests. In Thailand, Kitti’s hog-nosed bat is limited to a small area of the Tenasserim Hills in Sai Yok District, Kanchanaburi Province, in the drainage basin of the Khwae Noi River. While Sai Yok National Park in the Dawna Hills includes much of the bat’s area, some Thai communities happen outside the park and are unprotected.
Since the 2001 detection of a single individual in Myanmar, at least nine separate localities have been recognised in the limestone outcrops of the Dawna and Karen Hills outside the Thanlwin, Ataran, and Gyaing Rivers of Kayin and the Mon States. The Thai and Myanmar communities are morphologically equal, but their echolocation signals are distinct. It is not understood whether the two populations are reproductively separate.
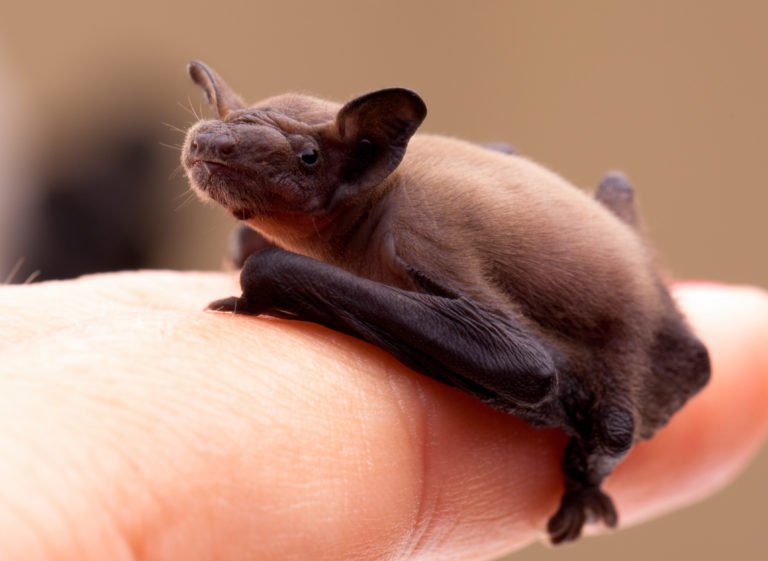

The Smallest Mammal in the World
How Small Are Bumblebee Bats?
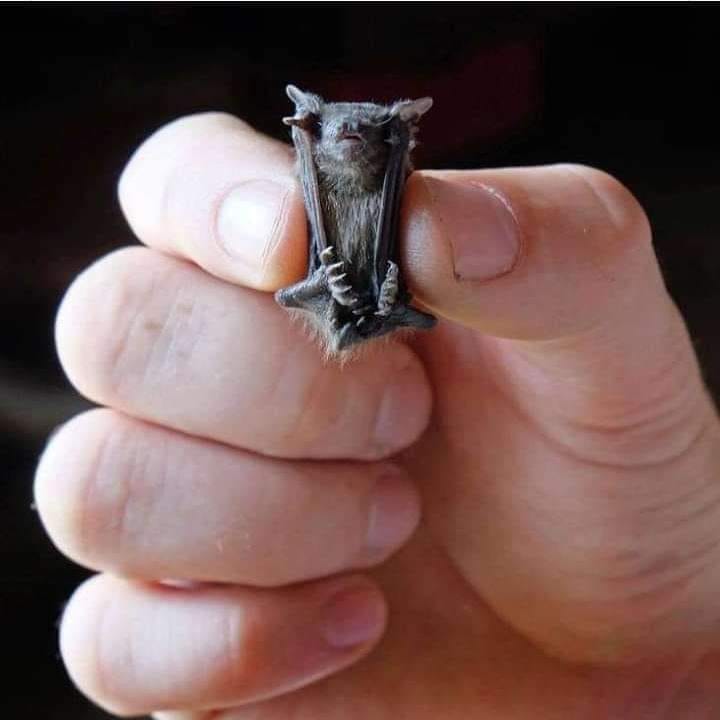
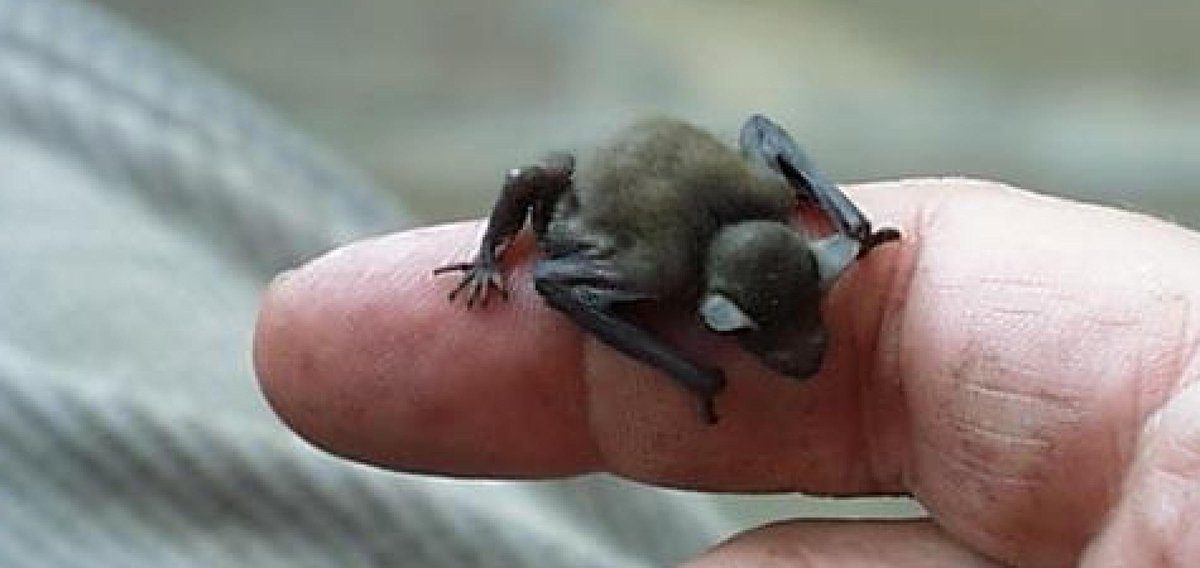
The head to body range of these bats is only 1.14 to 1.3 inches long (29 to 33 millimetres), earning them the tiniest known mammals in the world.
Their wingspan stretches 6.7 inches (170 mm). On average, they register a mere 0.7 ounces (2 grams).
What Do Bumblebee Bats Look Like
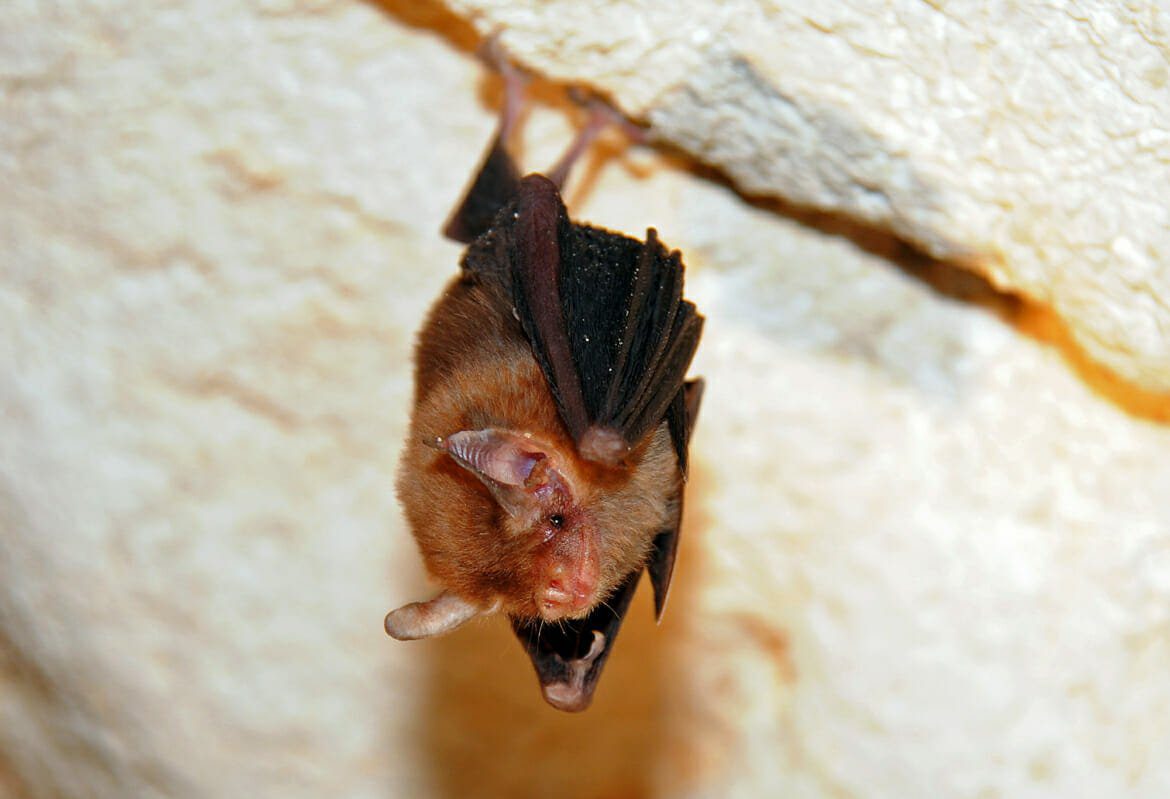
People usually describe bumblebee bats as possessing a pig-like face due to their big nostrils with a wide septum. This miniature brownish-red or grey bats possess a few unique physical features. Firstly, despite owning two caudal vertebrae, they don’t have a tail. Additionally, such tiny animals, have large ears averaging 0.4 inches (10.2 millimetres).
The males can be distinguished from the females by a significant swelling of a gland at the bottom of their throats. Females also have a secondary set of nipples near their groin. This other set of nipples seems to be vestigial as they no longer operate.

Bat Lifespan and Lifecycle
Otherwise known as Kitti’s hog-nosed bat, very little is understood about bumblebee bats’ lifespan and breeding behaviours. Based on comparable species, researchers suspect they live between five and 10 years. They are considered to have one offspring once a year and breed in the month of late April.
Social Life
These bats exist in roosts of 10 and up to 100 individuals. Residing in roosts is advantageous for keeping warm and locating mates. Despite these bats living in communities, they are not primarily sociable. Females roost solely in a nursery cave when raising offspring.
Diet and Food
These bats search in the bamboo forest canopies about their caves to find food. They essentially feast on insects.
Bats will accumulate the insects both by catching them mid-flight or nibbling them off of leaves. As insectivores, they can be helpful for humans as they can help limit insect pests in the region.

Perception and Observation
Like all other bats, the bumblebee bat utilises echolocation to see the world around them and obtain food. Bats release ultrasonic sounds from their nose or mouth. When the sound hits an object, it boomerangs back to the bat. The bats hear the sound to ascertain the size and shape of the thing in front of them.
Echolocation enables bats to see the world despite being in complete darkness. They can discover even the smallest of mosquitos to feed. Echolocation also prevents them from flying into objects.
Humans cannot detect the ultrasonic sounds bats emit for echolocation. Some prey animals such as moths can still understand when echolocation is being utilised and adjust their flight pattern to confuse the bats.
Bumblebee Bat Behavior & Characteristics
While little is understood about bumblebee bats, we know they function similarly to many other bat varieties. They are most active through dusk and dawn, although they manage to be active longer at dusk than dawn.
When they are not active, they are believed to enter states of inertia. During torpor, animals subdue their movement, body temperature and metabolic flow to save energy.

Conservation
As of the species’ most current review in 2019, Kitti’s hog-nosed bat is classified by the IUCN as near-threatened, with a descending population trend.
Soon following the bat’s discovery in the 1970s, some roosting positions became disturbed due to tourism, scientific samples, and even the collection and sale of the tiny bats as souvenirs.
Nevertheless, these pressures may not have had a notable effect on the species as a whole since many small colonies survive in hard-to-access areas, and only a few significant caves were disturbed. Another possible risk is the movement of local monks, who have invaded roost caves throughout periods of meditation.
The most notable and long-term threat to the Thai population may be the annual burning of forest regions, most widespread during the bat’s breeding season. In addition, the suggested construction of a pipeline from Myanmar to Thailand may have an adverse impact. Threats to the Myanmar population are not well recognised.
In the year 2007, the Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered Project classified Kitti’s hog-nosed bat as one of its Top 10 “focal species”.
Watch Bumblebee Bats Safely
Attending bat caves to see the worlds smallest mammal is enticing for many curious tourists, but it is possibly dangerous. Whilst guides and people may be induced to hold the tiny animals, this impedes the bats’ natural behaviours. If bitten, humans can catch diseases.
The best way to see those bats harmlessly is to visit the outside of one of the caverns in the National Park in Kanchanaburi Province, Thailand, at dusk or dawn to view them fly around feeding.































































